Abstract
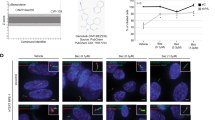
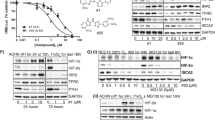
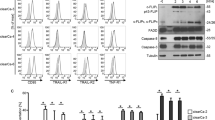
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CC-RCC) is the most lethal of all genitourinary cancers. The functional loss of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene occurs in 90% of CC-RCC, driving cancer progression. The objective of this study was to identify chemical compounds that are synthetically lethal with VHL deficiency in CC-RCC. An annotated chemical library, the library of pharmacologically active compounds (LOPAC), was screened in parallel on VHL-deficient RCC4 cells and RCC4VHL cells with re-introduced VHL. The ROCK inhibitor, Y-27632, was identified and validated for selective targeting of VHL-deficient CC-RCC in multiple genetic backgrounds by clonogenic assays. Downregulation of ROCK1 by small interfering RNA (siRNA) selectively reduced the colony-forming ability of VHL-deficient CC-RCC, thus mimicking the effect of Y-27632 treatment, whereas downregulation of ROCK2 had no effect. In addition, two other ROCK inhibitors, RKI 1447 and GSK 429286, selectively targeted VHL-deficient CC-RCC. CC-RCC treatment with ROCK inhibitors is cytotoxic and cytostatic based on bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) assay, propidium iodide (PI) staining and growth curves, and blocks cell migration based on transwell assay. On the one hand, knockdown of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) β in the VHL-deficient CC-RCC had a protective effect against Y-27632 treatment, mimicking VHL reintroduction. On the other hand, CC-RCCVHL cells were sensitized to Y-27632 treatment in hypoxia (2% O2). These results suggest that synthetic lethality between ROCK inhibition and VHL deficiency is dependent on HIF activation. Moreover, HIF1α or HIF2α overexpression in CC-RCCVHL cells is sufficient to sensitize them to ROCK inhibition. Finally, Y-27632 treatment inhibited growth of subcutaneous 786-OT1 CC-RCC tumors in mice. Thus, ROCK inhibitors represent potential therapeutics for VHL-deficient CC-RCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
analysis of variance
- ARNT:
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator
- BrdU:
-
Bromodeoxyuridine
- CC-RCC:
-
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- EYFP:
-
Enhanced Yellow Fluorescent Protein
- HA:
-
hemagglutinin
- HIF:
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor
- ip:
-
intraperitoneal
- LDHA:
-
Lactate Dehydrogenase A
- LOPAC:
-
Library of pharmacologically active compounds
- mTORi:
-
Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitors
- MYPT1:
-
Myosin Phosphatase Target 1
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- ROCK:
-
Rho-Associated, coiled-coil-containing protein kinase
- sc:
-
subcutaneous
- shRNA:
-
small hairpin RNA
- siRNA:
-
small interfering RNA
- VHL:
-
von Hippel-Lindau.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A . Cancer statistics 2016. Cancer J Clin 2016; 66: 7–30.
Motzer RJ, Russo P . Systemic therapy for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 2000; 163: 408–417.
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A . Cancer statistics 2014. Cancer J Clin 2014; 64: 9–29.
Hodorova I, Rybarova S . Multidrug resistance proteins in renal cell carcinoma. Folia Biol 2008; 192: 187–192.
Jonasch E, Futreal PA, Davis IJ, Bailey ST, Kim WY, Brugarolas J et al. State of the science: an update on renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res 2012; 10: 859–880.
Cowey CL, Rathmell WK . VHL gene mutations in renal cell carcinoma: role as a biomarker of disease outcome and drug efficacy. Curr Oncol Rep 2009; 11: 94–101.
Zhang Q, Yang H . The roles of VHL-dependent ubiquitination in signaling and cancer. Front Oncol 2012; 2: 1–7.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P . Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl JMed 2007; 356: 115–124.
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler W, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl JMed 2007; 456: 125–134.
Escudier B, Gore M . Axitinib for the management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Drugs R D 2011; 11: 113–126.
Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J et al. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 1061–1068.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Oudard S et al. Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 3584–3590.
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S et al. Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer 2010; 116: 4256–4265.
Hudes Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A et al. The global ARCC G. Temsirolimus, interferon alpha or both for advanced renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 2271–2281.
Pinto A . Adjuvant therapy for renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer 2014; 12: 408–412.
Rini BI, Atkins MB . Resistance to targeted therapy in renal-cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol 2009; 10: 992–1000.
Buczek M, Escudier B, Bartnik E, Szczylik C, Czarnecka A . Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: from the patient’s bed to molecular mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014; 1845: 31–41.
Chan D, Giaccia AJ . Harnessing synthetic lethal interactions in anticancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2011; 10: 351–364.
Thompson JM, Nguyen QH, Singh M, Razorenova O . Approaches to identifying synthetic lethal interactions in cancer. Yale J Biol Med 2015; 88: 1–11.
Chan Da, Sutphin PD, Nguyen P, Turcotte S, Lai EW, Banh A et al. Targeting GLUT1 and the Warburg effect in renal cell carcinoma by chemical synthetic lethality. Sci Transl Med 2011; 3: 94ra70.
Turcotte S, Chan D, Sutphin PD, Hay MP, Denny WA, Giaccia AJ . A molecule targeting VHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma that induces autophagy. Cancer Cell 2008; 14: 90–102.
Sutphin PD, Chan D, Li JM, Turcotte S, Krieg AJ, Giaccia AJ . Targeting the loss of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene in renal cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 5896–5905.
Woldemichael GM, Turbyville TJ, Vasselli JR, Linehan WM, McMahon JB . Lack of a functional VHL gene product sensitizes renal cell carcinoma cells to the apoptotic effects of the protein synthesis inhibitor verrucarin A. Neoplasia 2012; 14: 771–777.
Wolff NC, Pavía-Jiménez A, Tcheuyap VT, Alexander S, Vishwanath M, Christie A et al. High-throughput simultaneous screen and counterscreen identifies homoharringtonine as synthetic lethal with von Hippel-Lindau loss in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 16951–16962.
Bommi-Reddy A, Almeciga I, Sawyer J, Geisen C, Li W, Harlow E et al. Kinase requirements in human cells: III. Altered kinase requirements in VHL-/- cancer cells detected in a pilot synthetic lethal screen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 16484–16489.
Shi J, Wu X, Surma M, Vemula S, Zhang L, Yang Y et al. Distinct roles for ROCK1 and ROCK2 in the regulation of cell detachment. Cell Death Dis 2013; 4: e483.
Kamai T, Tsujii T, Arai K . Significant association of Rho / ROCK pathway with invasion and metastasis of bladder cancer significant association of Rho / ROCK pathway with invasion and metastasis of bladder cancer 1. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 2632–2641.
Kamai T, Yamanishi T, Shirataki H, Takagi K, Asami H, Ito Y et al. Overexpression of RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42 GTPases is associated with progression in testicular cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 4799–4805.
Lane J, Martin T, Watkins G, Mansel R, Jiang W . The expression and prognostic value of ROCK I and ROCK II and their role in human breast cancer. Int J Oncol 2008; 33: 585–593.
Zhang C, Zhang S, Zhang Z, He J, Xu Y, Liu S . ROCK has a crucial role in regulating prostate tumor growth through interaction with c-Myc. Oncogene 2014; 33: 5582–5591.
Abe H, Kamai T, Tsujii T, Nakamura F, Mashidori T, Mizuno T et al. Possible role of the RhoC/ROCK pathway in progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Biomed Res 2008; 29: 155–161.
Liu S, Goldstein RH, Scepansky EM, Rosenblatt M . Inhibition of rho-associated kinase signaling prevents breast cancer metastasis to human bone. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 8742–8751.
Liao JK, Seto M, Noma K . Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2007; 50: 17–24.
Mleczak A, Millar S, Tooze SA, Olson MF, Chan EYW . Regulation of autophagosome formation by Rho kinase. Cell Signal 2013; 25: 1–11.
Nakagawa O, Fujisawa K, Ishizaki T, Saito Y, Nakao K, Narumiya S . ROCK-I and ROCK-II, two isoforms of Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein serine/threonine kinase in mice. FEBS Lett 1996; 392: 189–193.
Razorenova O, Castellini L, Colavitti R, Edgington LE, Nicolau M, Huang X et al. The apoptosis repressor with a CARD domain (ARC) gene is a direct hypoxia-inducible factor 1 target gene and promotes survival and proliferation of VHL-deficient renal cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol 2014; 34: 739–751.
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME et al. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 1999; 399: 271–275.
Chan D, Sutphin PD, Denko NC, Giaccia AJ . Role of prolyl hydroxylation in oncogenically stabilized hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 40112–40117.
Amin E, Dubey BN, Zhang SC, Gremer L, Dvorsky R, Moll JM et al. Rho-kinase: regulation, (dys)function, and inhibition. Biol Chem 2013; 394: 1399–1410.
Patel R, Forinash KD, Pireddu R, Sun Y, Sun N, Martin MP et al. RKI-1447 is a potent inhibitor of the Rho-associated ROCK kinases with anti-invasive and antitumor activities in breast cancer. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 5025–5034.
Isler D, Ozaslan M, Karagoz ID, Kilic IH, Karakok M, Taysi S et al. Antitumoral effect of a selective Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma in mice. Pharmacol Rep 2014; 66: 114–120.
Rikitake Y, Kim H-H, Huang Z, Seto M, Yano K, Asano T et al. Inhibition of Rho kinase (ROCK) leads to increased cerebral blood flow and stroke protection. Stroke 2005; 36: 2251–2257.
Inan S, Büyükafşar K . Antiepileptic effects of two Rho-kinase inhibitors, Y-27632 and fasudil, in mice. Br J Pharmacol 2008; 155: 44–51.
Nagatoya K, Moriyama T, Kawada N, Takeji M, Oseto S, Murozono T et al. Y-27632 prevents tubulointerstitial fibrosis in mouse kidneys with unilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int 2002; 61: 1684–1695.
Gordan J, Lal P, Dondeti V, Letrero R . HIF-α effects on c-Myc distinguish two subtypes of sporadic VHL-deficient clear cell renal carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2008; 14: 435–446.
Lochhead P, Wickman G, Mezna M, Olson MF . Activating ROCK1 somatic mutations in human cancer. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2591–2598.
Liu X, Choy E, Hornicek FJ, Yang S, Yang C, Harmon D et al. ROCK1 as a potential therapeutic target in osteosarcoma. J Orthop Res 2011; 29: 1259–1266.
Semenza GL . Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 721–732.
Kapitsinou PP, Haase VH . The VHL tumor suppressor and HIF: insights from genetic studies in mice. Cell Death Differ 2008; 15: 650–659.
Gilkes DM, Xiang L, Lee SJ, Chaturvedi P, Hubbi ME, Wirtz D et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors mediate coordinated RhoA-ROCK1 expression and signaling in breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 111: E384–E393.
Greijer AE, van der Groep P, Kemming D, Shvarts A, Semenza GL, Meijer GA et al. Up-regualtion of gene expression by hypoxia is mediated predominantly by hypoxia-inducible factor I (HIF-I). J Pathol 2005; 206: 291–304.
Turcotte S . HIF-1alpha mRNA and protein upregulation involves Rho GTPase expression during hypoxia in renal cell carcinoma. J Cell Sci 2003; 116: 2247–2260.
Takata K, Morishige K-I, Takahashi T, Hashimoto K, Tsutsumi S, Yin L et al. Fasudil-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha degradation disrupts a hypoxia-driven vascular endothelial growth factor autocrine mechanism in endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 1551–1561.
Mizukami Y, Fujiki K, Duerr E-M, Gala M, Jo W-S, Zhang X et al. Hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor through the induction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Rho/ROCK and c-Myc. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 13957–13963.
Razorenova O, Finger E, Colavitti R, Chernikova S, Boiko A, Chan C et al. VHL loss in renal cell carcinoma leads to up-regulation of CUB domain-containing protein 1 to stimulate PKC{delta}-driven migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 1931–1936.
Razorenova O, Ivanov V, Budanov V, Chumakov P . Virus-based reporter systems for monitoring transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Gene 2005; 350: 89–98.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by ACS-IRG-98-279-10 and NCI R03 CA202563-01 to OVR, NIH T32 (2T32CA009054-36A1) to JMT, NIH T32 NS82174-3 to IN and NIH ICTS (UL1 TR001414) to LJN. We thank Dr David Fruman and Dr Hung Fan for critical reading of the manuscript and anonymous reviewers for constructive critique.
Author contributions
OVR and JMT designed the study. JMT, QHN, MS, MWP, IN, LJN, ACL and OVR conducted experiments and analyzed the data. JMT and OVR wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, J., Nguyen, Q., Singh, M. et al. Rho-associated kinase 1 inhibition is synthetically lethal with von Hippel-Lindau deficiency in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 36, 1080–1089 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.272
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.272