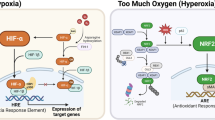
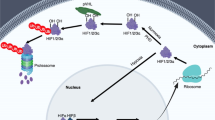
Abstract
Hypoxia is an imbalance between oxygen supply and demand, which deprives cells or tissues of sufficient oxygen. It is well-established that hypoxia triggers adaptive responses, which contribute to short- and long-term pathologies such as inflammation, cardiovascular disease and cancer. Induced by both microenvironmental hypoxia and genetic mutations, the elevated expression of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 is a key feature of many human cancers and has been shown to promote cellular processes, which facilitate tumor progression. In this review, we discuss the emerging role of hypoxia and the HIFs in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma (MM), an incurable hematological malignancy of BM PCs, which reside within the hypoxic BM microenvironment. The need for current and future therapeutic interventions to target HIF-1 and HIF-2 in myeloma will also be discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grogan TM, Muller-Hermelink HK, Van Camp B, Harris NL, Kyle RA . Plasma cell neoplasms: mature B-cell neoplasms. In: Jaffe ES HN, Stein H, Vardiman JW (eds). World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, vol. 3, IARC Press: Lyon, 2001, pp 142–156.
Kumar SK, Rajkumar SV, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR, Buadi FK et al. Improved survival in multiple myeloma and the impact of novel therapies. Blood 2008; 111: 2516–2520.
Jiang BH, Zheng JZ, Leung SW, Roe R, Semenza GL . Transactivation and inhibitory domains of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Modulation of transcriptional activity by oxygen tension. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 19253–19260.
Manalo DJ, Rowan A, Lavoie T, Natarajan L, Kelly BD, Ye SQ et al. Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial cell responses to hypoxia by HIF-1. Blood 2005; 105: 659–669.
Semenza G . Signal transduction to hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Biochem Pharmacol 2002; 64: 993–998.
Semenza GL . Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 721–732.
Semenza GL . Angiogenesis in ischemic and neoplastic disorders. Annu Rev Med 2003; 54: 17–28.
Brown JM, Wilson WR . Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 437–447.
Goda F, O'Hara JA, Liu KJ, Rhodes ES, Dunn JF, Swartz HM . Comparisons of measurements of pO2 in tissue in vivo by EPR oximetry and microelectrodes. Adv Exp Med Biol 1997; 411: 543–549.
Hockel M, Vaupel P . Tumor hypoxia: definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001; 93: 266–276.
Cooper RA, Carrington BM, Loncaster JA, Todd SM, Davidson SE, Logue JP et al. Tumour oxygenation levels correlate with dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging parameters in carcinoma of the cervix. Radiother Oncol 2000; 57: 53–59.
Dewhirst MW, Klitzman B, Braun RD, Brizel DM, Haroon ZA, Secomb TW . Review of methods used to study oxygen transport at the microcirculatory level. Int J Cancer 2000; 90: 237–255.
Rofstad EK, Galappathi K, Mathiesen B, Ruud EB . Fluctuating and diffusion-limited hypoxia in hypoxia-induced metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 1971–1978.
Le QT, Denko NC, Giaccia AJ . Hypoxic gene expression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2004; 23: 293–310.
Subarsky P, Hill RP . The hypoxic tumour microenvironment and metastatic progression. Clin Exp Metastasis 2003; 20: 237–250.
Brizel DM, Scully SP, Harrelson JM, Layfield LJ, Bean JM, Prosnitz LR et al. Tumor oxygenation predicts for the likelihood of distant metastases in human soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 941–943.
Harris AL . Hypoxia—a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 38–47.
Hockel M, Schlenger K, Hockel S, Vaupel P . Hypoxic cervical cancers with low apoptotic index are highly aggressive. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 4525–4528.
Cairns RA, Hill RP . Acute hypoxia enhances spontaneous lymph node metastasis in an orthotopic murine model of human cervical carcinoma. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 2054–2061.
Cairns RA, Kalliomaki T, Hill RP . Acute (cyclic) hypoxia enhances spontaneous metastasis of KHT murine tumors. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 8903–8908.
Rofstad EK, Mathiesen B, Henriksen K, Kindem K, Galappathi K . The tumor bed effect: increased metastatic dissemination from hypoxia-induced upregulation of metastasis-promoting gene products. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 2387–2396.
Rofstad EK, Rasmussen H, Galappathi K, Mathiesen B, Nilsen K, Graff BA . Hypoxia promotes lymph node metastasis in human melanoma xenografts by up-regulating the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 1847–1853.
Chi JT, Wang Z, Nuyten DS, Rodriguez EH, Schaner ME, Salim A et al. Gene expression programs in response to hypoxia: cell type specificity and prognostic significance in human cancers. PLoS Med 2006; 3: e47.
Wang GL, Semenza GL . Characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and regulation of DNA binding activity by hypoxia. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 21513–21518.
Wiesener MS, Turley H, Allen WE, Willam C, Eckardt KU, Talks KL et al. Induction of endothelial PAS domain protein-1 by hypoxia: characterization and comparison with hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Blood 1998; 92: 2260–2268.
Oikawa M, Abe M, Kurosawa H, Hida W, Shirato K, Sato Y . Hypoxia induces transcription factor ETS-1 via the activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 289: 39–43.
Taylor CT, Furuta GT, Synnestvedt K, Colgan SP . Phosphorylation-dependent targeting of cAMP response element binding protein to the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway in hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 12091–12096.
Bandyopadhyay RS, Phelan M, Faller DV . Hypoxia induces AP-1-regulated genes and AP-1 transcription factor binding in human endothelial and other cell types. Biochim Biophys Acta 1995; 1264: 72–78.
Rupec RA, Baeuerle PA . The genomic response of tumor cells to hypoxia and reoxygenation. Differential activation of transcription factors AP-1 and NF-kappa B. Eur J Biochem 1995; 234: 632–640.
Yao KS, Xanthoudakis S, Curran T, O'Dwyer PJ . Activation of AP-1 and of a nuclear redox factor, Ref-1, in the response of HT29 colon cancer cells to hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol 1994; 14: 5997–6003.
Schmedtje Jr JF, Ji YS, Liu WL, DuBois RN, Runge MS . Hypoxia induces cyclooxygenase-2 via the NF-kappaB p65 transcription factor in human vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 601–608.
Semenza GL . Hydroxylation of HIF-1: oxygen sensing at the molecular level. Physiology (Bethesda) 2004; 19: 176–182.
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL . Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix–loop–helix–PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 5510–5514.
Kallio PJ, Wilson WJ, O'Brien S, Makino Y, Poellinger L . Regulation of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1alpha by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 6519–6525.
Semenza GL . Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: oxygen homeostasis and disease pathophysiology. Trends Mol Med 2001; 7: 345–350.
Maynard MA, Qi H, Chung J, Lee EH, Kondo Y, Hara S et al. Multiple splice variants of the human HIF-3 alpha locus are targets of the von Hippel–Lindau E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 11032–11040.
Huang LE, Arany Z, Livingston DM, Bunn HF . Activation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor depends primarily upon redox-sensitive stabilization of its alpha subunit. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 32253–32259.
Huang LE, Gu J, Schau M, Bunn HF . Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is mediated by an O2-dependent degradation domain via the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 7987–7992.
Kallio PJ, Pongratz I, Gradin K, McGuire J, Poellinger L . Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha: posttranscriptional regulation and conformational change by recruitment of the Arnt transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 5667–5672.
Powell JD, Elshtein R, Forest DJ, Palladino MA . Stimulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein in the adult rat testis following ischemic injury occurs without an increase in HIF-1alpha messenger RNA expression. Biol Reprod 2002; 67: 995–1002.
Wenger RH, Kvietikova I, Rolfs A, Gassmann M, Marti HH . Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha is regulated at the post-mRNA level. Kidney Int 1997; 51: 560–563.
Salceda SaC J . Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein is rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin–proteasome system under normoxic conditions. Its stabilization by hypoxia depends on redox-induced changes. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 22642–22647.
Lando D, Peet DJ, Gorman JJ, Whelan DA, Whitelaw ML, Bruick RK . FIH-1 is an asparaginyl hydroxylase enzyme that regulates the transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor. Genes Dev 2002; 16: 1466–1471.
Jiang BH, Rue E, Wang GL, Roe R, Semenza GL . Dimerization, DNA binding, and transactivation properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 17771–17778.
Carrero P, Okamoto K, Coumailleau P, O'Brien S, Tanaka H, Poellinger L . Redox-regulated recruitment of the transcriptional coactivators CREB-binding protein and SRC-1 to hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 402–415.
Okino ST, Chichester CH, Whitlock Jr JP . Hypoxia-inducible mammalian gene expression analyzed in vivo at a TATA-driven promoter and at an initiator-driven promoter. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 23837–23843.
Richard DE, Berra E, Gothie E, Roux D, Pouyssegur J . p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 32631–32637.
Semenza GL . HIF-1: mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 2000; 88: 1474–1480.
Motzer RJ, Bander NH, Nanus DM . Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1996; 335: 865–875.
Blagosklonny MV, An WG, Romanova LY, Trepel J, Fojo T, Neckers L . p53 inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-stimulated transcription. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 11995–11998.
Zundel W, Schindler C, Haas-Kogan D, Koong A, Kaper F, Chen E et al. Loss of PTEN facilitates HIF-1-mediated gene expression. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 391–396.
Blancher C, Moore JW, Robertson N, Harris AL . Effects of ras and von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) gene mutations on hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, and vascular endothelial growth factor expression and their regulation by the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 7349–7355.
Dang CV, Kim JW, Gao P, Yustein J . The interplay between MYC and HIF in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 51–56.
Kikuchi H, Pino MS, Zeng M, Shirasawa S, Chung DC . Oncogenic KRAS and BRAF differentially regulate hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha in colon cancer. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 8499–8506.
Ceradini DJ, Kulkarni AR, Callaghan MJ, Tepper OM, Bastidas N, Kleinman ME et al. Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat Med 2004; 10: 858–864.
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, Laughner E, Hanrahan C, Georgescu MM et al. Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 1541–1545.
Feldser D, Agani F, Iyer NV, Pak B, Ferreira G, Semenza GL . Reciprocal positive regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and insulin-like growth factor 2. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 3915–3918.
Richard DE, Berra E, Pouyssegur J . Nonhypoxic pathway mediates the induction of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 26765–26771.
Gorlach A, Diebold I, Schini-Kerth VB, Berchner-Pfannschmidt U, Roth U, Brandes RP et al. Thrombin activates the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells: role of the p22(phox)-containing NADPH oxidase. Circ Res 2001; 89: 47–54.
Hellwig-Burgel T, Rutkowski K, Metzen E, Fandrey J, Jelkmann W . Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulate DNA binding of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Blood 1999; 94: 1561–1567.
Dery MA, Michaud MD, Richard DE . Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: regulation by hypoxic and non-hypoxic activators. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2005; 37: 535–540.
Gao P, Zhang H, Dinavahi R, Li F, Xiang Y, Raman V et al. HIF-dependent antitumorigenic effect of antioxidants in vivo. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 230–238.
Quintero M, Brennan PA, Thomas GJ, Moncada S . Nitric oxide is a factor in the stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in cancer: role of free radical formation. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 770–774.
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M, Hilton DA, Zagzag D et al. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 5830–5835.
Talks KL, Turley H, Gatter KC, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ et al. The expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated macrophages. Am J Pathol 2000; 157: 411–421.
Zagzag D, Zhong H, Scalzitti JM, Laughner E, Simons JW, Semenza GL . Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in brain tumors: association with angiogenesis, invasion, and progression. Cancer 2000; 88: 2606–2618.
Volm M, Koomagi R . Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) and its relationship to apoptosis and proliferation in lung cancer. Anticancer Res 2000; 20: 1527–1533.
Bos R, Zhong H, Hanrahan CF, Mommers EC, Semenza GL, Pinedo HM et al. Levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha during breast carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001; 93: 309–314.
Turner KJ, Moore JW, Jones A, Taylor CF, Cuthbert-Heavens D, Han C et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factors in human renal cancer: relationship to angiogenesis and to the von Hippel–Lindau gene mutation. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 2957–2961.
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Sivridis E, Turley H, Talks K, Pezzella F et al. Relation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and 2 alpha in operable non-small cell lung cancer to angiogenic/molecular profile of tumours and survival. Br J Cancer 2001; 85: 881–890.
Birner P, Gatterbauer B, Oberhuber G, Schindl M, Rossler K, Prodinger A et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in oligodendrogliomas: its impact on prognosis and on neoangiogenesis. Cancer 2001; 92: 165–171.
Bos R, van der Groep P, Greijer AE, Shvarts A, Meijer S, Pinedo HM et al. Levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha independently predict prognosis in patients with lymph node negative breast carcinoma. Cancer 2003; 97: 1573–1581.
Nakanishi K, Hiroi S, Tominaga S, Aida S, Kasamatsu H, Matsuyama S et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein predicts survival in patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 2583–2590.
Shibaji T, Nagao M, Ikeda N, Kanehiro H, Hisanaga M, Ko S et al. Prognostic significance of HIF-1 alpha overexpression in human pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res 2003; 23: 4721–4727.
Theodoropoulos VE, Lazaris A, Sofras F, Gerzelis I, Tsoukala V, Ghikonti I et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha expression correlates with angiogenesis and unfavorable prognosis in bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2004; 46: 200–208.
Yang QC, Zeng BF, Dong Y, Shi ZM, Jiang ZM, Huang J . Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in human osteosarcoma: correlation with clinicopathological parameters and survival outcome. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2007; 37: 127–134.
Evens AM, Schumacker PT, Helenowski IB, Singh AT, Dokic D, Keswani A et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-alpha activation in lymphoma and relationship to the thioredoxin family. Br J Haematol 2008; 141: 676–680.
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Pezzella F, Sivridis E, Turley H, Harris AL et al. Phosphorylated VEGFR2/KDR receptors are widely expressed in B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and correlate with hypoxia inducible factor activation. Hematol Oncol 2008; 26: 219–224.
Frater JL, Kay NE, Goolsby CL, Crawford SE, Dewald GW, Peterson LC . Dysregulated angiogenesis in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia: morphologic, immunohistochemical, and flow cytometric evidence. Diagn Pathol 2008; 3: 16.
Wellmann S, Guschmann M, Griethe W, Eckert C, von Stackelberg A, Lottaz C et al. Activation of the HIF pathway in childhood ALL, prognostic implications of VEGF. Leukemia 2004; 18: 926–933.
Peng J, Zhang L, Drysdale L, Fong GH . The transcription factor EPAS-1/hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha plays an important role in vascular remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 8386–8391.
Yu AY, Shimoda LA, Iyer NV, Huso DL, Sun X, McWilliams R et al. Impaired physiological responses to chronic hypoxia in mice partially deficient for hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. J Clin Invest 1999; 103: 691–696.
Iyer NV, Kotch LE, Agani F, Leung SW, Laughner E, Wenger RH et al. Cellular and developmental control of O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Genes Dev 1998; 12: 149–162.
Scortegagna M, Ding K, Oktay Y, Gaur A, Thurmond F, Yan LJ et al. Multiple organ pathology, metabolic abnormalities and impaired homeostasis of reactive oxygen species in Epas1−/− mice. Nat Genet 2003; 35: 331–340.
Camenisch G, Stroka DM, Gassmann M, Wenger RH . Attenuation of HIF-1 DNA-binding activity limits hypoxia-inducible endothelin-1 expression. Pflugers Arch 2001; 443: 240–249.
Tian H, McKnight SL, Russell DW . Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 (EPAS1), a transcription factor selectively expressed in endothelial cells. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 72–82.
Hu CJ, Wang LY, Chodosh LA, Keith B, Simon MC . Differential roles of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in hypoxic gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 9361–9374.
Sowter HM, Raval RR, Moore JW, Ratcliffe PJ, Harris AL . Predominant role of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (Hif)-1alpha versus Hif-2alpha in regulation of the transcriptional response to hypoxia. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 6130–6134.
Ema M, Taya S, Yokotani N, Sogawa K, Matsuda Y, Fujii-Kuriyama Y . A novel bHLH–PAS factor with close sequence similarity to hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha regulates the VEGF expression and is potentially involved in lung and vascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 4273–4278.
Tian H, Hammer RE, Matsumoto AM, Russell DW, McKnight SL . The hypoxia-responsive transcription factor EPAS1 is essential for catecholamine homeostasis and protection against heart failure during embryonic development. Genes Dev 1998; 12: 3320–3324.
Wiesener MS, Jurgensen JS, Rosenberger C, Scholze CK, Horstrup JH, Warnecke C et al. Widespread hypoxia-inducible expression of HIF-2alpha in distinct cell populations of different organs. FASEB J 2003; 17: 271–273.
Chavez JC, Baranova O, Lin J, Pichiule P . The transcriptional activator hypoxia inducible factor 2 (HIF-2/EPAS-1) regulates the oxygen-dependent expression of erythropoietin in cortical astrocytes. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 9471–9481.
Bracken CP, Fedele AO, Linke S, Balrak W, Lisy K, Whitelaw ML et al. Cell-specific regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-2alpha stabilization and transactivation in a graded oxygen environment. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 22575–22585.
Hu CJ, Iyer S, Sataur A, Covello KL, Chodosh LA, Simon MC . Differential regulation of the transcriptional activities of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in stem cells. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 3514–3526.
Hu CJ, Sataur A, Wang L, Chen H, Simon MC . The N-terminal transactivation domain confers target gene specificity of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha. Mol Biol Cell 2007; 18: 4528–4542.
Berra E, Benizri E, Ginouves A, Volmat V, Roux D, Pouyssegur J . HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1alpha in normoxia. EMBO J 2003; 22: 4082–4090.
Bishop T, Gallagher D, Pascual A, Lygate CA, de Bono JP, Nicholls LG et al. Abnormal sympathoadrenal development and systemic hypotension in PHD3−/− mice. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 3386–3400.
Shichijo S, Nakao M, Imai Y, Takasu H, Kawamoto M, Niiya F et al. A gene encoding antigenic peptides of human squamous cell carcinoma recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med 1998; 187: 277–288.
Koh MY, Darnay BG, Powis G . Hypoxia-associated factor, a novel E3-ubiquitin ligase, binds and ubiquitinates hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha, leading to its oxygen-independent degradation. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 7081–7095.
Chen L, Uchida K, Endler A, Shibasaki F . Mammalian tumor suppressor Int6 specifically targets hypoxia inducible factor 2 alpha for degradation by hypoxia- and pVHL-independent regulation. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 12707–12716.
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ, Simon MC . Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell 2010; 40: 294–309.
Bertout JA, Patel SA, Simon MC . The impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 967–975.
Raval RR, Lau KW, Tran MG, Sowter HM, Mandriota SJ, Li JL et al. Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in von Hippel–Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 5675–5686.
An WG, Kanekal M, Simon MC, Maltepe E, Blagosklonny MV, Neckers LM . Stabilization of wild-type p53 by hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Nature 1998; 392: 405–408.
Roberts AM, Watson IR, Evans AJ, Foster DA, Irwin MS, Ohh M . Suppression of hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha restores p53 activity via Hdm2 and reverses chemoresistance of renal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 9056–9064.
Pennathur-Das R, Levitt L . Augmentation of in vitro human marrow erythropoiesis under physiological oxygen tensions is mediated by monocytes and T lymphocytes. Blood 1987; 69: 899–907.
Danet GH, Pan Y, Luongo JL, Bonnet DA, Simon MC . Expansion of human SCID-repopulating cells under hypoxic conditions. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 126–135.
Watanabe Y, Terashima Y, Takenaka N, Kobayashi M, Matsushita T . Prediction of avascular necrosis of the femoral head by measuring intramedullary oxygen tension after femoral neck fracture. J Orthop Trauma 2007; 21: 456–461.
Tondevold E, Eriksen J, Jansen E . Observations on long bone medullary pressure in relation to mean arterial blood pressure in the anaesthetized dog. Acta Orthop Scand 1979; 50: 527–531.
Colla S, Storti P, Donofrio G, Todoerti K, Bolzoni M, Lazzaretti M et al. Low bone marrow oxygen tension and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha overexpression characterize patients with multiple myeloma: role on the transcriptional and proangiogenic profiles of CD138(+) cells. Leukemia 2010; 24: 1967–1970.
Parmar K, Mauch P, Vergilio JA, Sackstein R, Down JD . Distribution of hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow according to regional hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 5431–5436.
Levesque JP, Winkler IG, Hendy J, Williams B, Helwani F, Barbier V et al. Hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization results in hypoxia with increased hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1 alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor A in bone marrow. Stem Cells 2007; 25: 1954–1965.
Hu J, Handisides DR, Van Valckenborgh E, De Raeve H, Menu E, Vande Broek I et al. Targeting the multiple myeloma hypoxic niche with TH-302, a hypoxia-activated prodrug. Blood 2010; 116: 1524–1527.
Wilson A, Trumpp A . Bone-marrow haematopoietic-stem-cell niches. Nat Rev Immunol 2006; 6: 93–106.
Asosingh K, De Raeve H, de Ridder M, Storme GA, Willems A, Van Riet I et al. Role of the hypoxic bone marrow microenvironment in 5T2MM murine myeloma tumor progression. Haematologica 2005; 90: 810–817.
Galluzzo M, Pennacchietti S, Rosano S, Comoglio PM, Michieli P . Prevention of hypoxia by myoglobin expression in human tumor cells promotes differentiation and inhibits metastasis. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 865–875.
Martin SK, Diamond P, Williams SA, To LB, Peet DJ, Fujii N et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2 is a novel regulator of aberrant CXCL12 expression in multiple myeloma plasma cells. Haematologica 2010; 95: 776–784.
Giatromanolaki A, Bai M, Margaritis D, Bourantas KL, Koukourakis MI, Sivridis E et al. Hypoxia and activated VEGF/receptor pathway in multiple myeloma. Anticancer Res 2010; 30: 2831–2836.
Holmquist-Mengelbier L, Fredlund E, Lofstedt T, Noguera R, Navarro S, Nilsson H et al. Recruitment of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha to common target genes is differentially regulated in neuroblastoma: HIF-2alpha promotes an aggressive phenotype. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 413–423.
Lofstedt T, Fredlund E, Holmquist-Mengelbier L, Pietras A, Ovenberger M, Poellinger L et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-2alpha in cancer. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 2007; 6: 919–926.
Patel SA, Simon MC . Biology of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha in development and disease. Cell Death Differ 2008; 15: 628–634.
Kaluz S, Kaluzova M, Stanbridge EJ . Proteasomal inhibition attenuates transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) via specific effect on the HIF-1alpha C-terminal activation domain. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 5895–5907.
Shin DH, Chun YS, Lee DS, Huang LE, Park JW . Bortezomib inhibits tumor adaptation to hypoxia by stimulating the FIH-mediated repression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Blood 2008; 111: 3131–3136.
Zhang J, Sattler M, Tonon G, Grabher C, Lababidi S, Zimmerhackl A et al. Targeting angiogenesis via a c-Myc/hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-dependent pathway in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 5082–5090.
Lu L, Payvandi F, Wu L, Zhang LH, Hariri RJ, Man HW et al. The anticancer drug lenalidomide inhibits angiogenesis and metastasis via multiple inhibitory effects on endothelial cell function in normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Microvasc Res 2009; 77: 78–86.
Ria R, Reale A, Berardi S, Piccoli C, Di Pietro G, Basile A et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in multiple myeloma progression [abstract]. Blood 2009; 114; abstract 1812.
Bozec A, Bakiri L, Hoebertz A, Eferl R, Schilling AF, Komnenovic V et al. Osteoclast size is controlled by Fra-2 through LIF/LIF-receptor signalling and hypoxia. Nature 2008; 454: 221–225.
Colla S, Tagliaferri S, Morandi F, Lunghi P, Donofrio G, Martorana D et al. The new tumor-suppressor gene inhibitor of growth family member 4 (ING4) regulates the production of proangiogenic molecules by myeloma cells and suppresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) activity: involvement in myeloma-induced angiogenesis. Blood 2007; 110: 4464–4475.
Hatzimichael E, Dasoula A, Shah R, Syed N, Papoudou-Bai A, Coley HM et al. The prolyl-hydroxylase EGLN3 and not EGLN1 is inactivated by methylation in plasma cell neoplasia. Eur J Haematol 2009; 84: 47–51.
Shou Y, Martelli ML, Gabrea A, Qi Y, Brents LA, Roschke A et al. Diverse karyotypic abnormalities of the c-myc locus associated with c-myc dysregulation and tumor progression in multiple myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 228–233.
Simon JA, Bedalov A . Yeast as a model system for anticancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 481–492.
Welsh S, Williams R, Kirkpatrick L, Paine-Murrieta G, Powis G . Antitumor activity and pharmacodynamic properties of PX-478, an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Mol Cancer Ther 2004; 3: 233–244.
Greenberger LM, Horak ID, Filpula D, Sapra P, Westergaard M, Frydenlund HF et al. A RNA antagonist of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, EZN-2968, inhibits tumor cell growth. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 3598–3608.
Duan JX, Jiao H, Kaizerman J, Stanton T, Evans JW, Lan L et al. Potent and highly selective hypoxia-activated achiral phosphoramidate mustards as anticancer drugs. J Med Chem 2008; 51: 2412–2420.
Bendell JC, Weiss GJ, Infante JR, Chiorean EG, Borad M, Ribes R et al. Final results of a phase I study of TH-302, a hypoxia-activated cytotoxic prodrug (HAP). J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 2573.
Hu Y, Kirito K, Yoshida K, Mitsumori T, Nakajima K, Nozaki Y et al. Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 function enhances the sensitivity of multiple myeloma cells to melphalan. Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8: 2329–2338.
Heider U, Hofbauer LC, Zavrski I, Kaiser M, Jakob C, Sezer O . Novel aspects of osteoclast activation and osteoblast inhibition in myeloma bone disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 338: 687–693.
Palayoor ST, Mitchell JB, Cerna D, Degraff W, John-Aryankalayil M, Coleman CN . PX-478, an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, enhances radiosensitivity of prostate carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 2008; 123: 2430–2437.
Vinson C . A rationally designed small molecule that inhibits the HIF-1alpha-ARNT heterodimer from binding to DNA in vivo. Sci STKE 2005; 2005: pe23.
Yeo EJ, Chun YS, Cho YS, Kim J, Lee JC, Kim MS et al. YC-1: a potential anticancer drug targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Natl Cancer Inst 2003; 95: 516–525.
Sun HL, Liu YN, Huang YT, Pan SL, Huang DY, Guh JH et al. YC-1 inhibits HIF-1 expression in prostate cancer cells: contribution of Akt/NF-kappaB signaling to HIF-1alpha accumulation during hypoxia. Oncogene 2007; 26: 3941–3951.
Zhao Q, Du J, Gu H, Teng X, Zhang Q, Qin H et al. Effects of YC-1 on hypoxia-inducible factor 1-driven transcription activity, cell proliferative vitality, and apoptosis in hypoxic human pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreas 2007; 34: 242–247.
Palayoor ST, Tofilon PJ, Coleman CN . Ibuprofen-mediated reduction of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in prostate cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 3150–3157.
Wang J, Wu K, Bai F, Zhai H, Xie H, Du Y et al. Celecoxib could reverse the hypoxia-induced Angiopoietin-2 upregulation in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett 2006; 242: 20–27.
Zhong H, Willard M, Simons J . NS398 reduces hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-1 activity: multiple-level effects involving cyclooxygenase-2 dependent and independent mechanisms. Int J Cancer 2004; 112: 585–595.
Mabjeesh NJ, Post DE, Willard MT, Kaur B, Van Meir EG, Simons JW et al. Geldanamycin induces degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha protein via the proteosome pathway in prostate cancer cells. Cancer research 2002; 62: 2478–2482.
Laughner E, Taghavi P, Chiles K, Mahon PC, Semenza GL . HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) synthesis: novel mechanism for HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 3995–4004.
Litz J, Krystal GW . Imatinib inhibits c-Kit-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha activity and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2006; 5: 1415–1422.
Luwor RB, Lu Y, Li X, Mendelsohn J, Fan Z . The antiepidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab/C225 reduces hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha, leading to transcriptional inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Oncogene 2005; 24: 4433–4441.
Mayerhofer M, Valent P, Sperr WR, Griffin JD, Sillaber C . BCR/ABL induces expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its transcriptional activator, hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha, through a pathway involving phosphoinositide 3-kinase and the mammalian target of rapamycin. Blood 2002; 100: 3767–3775.
Pore N, Jiang Z, Gupta A, Cerniglia G, Kao GD, Maity A . EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors decrease VEGF expression by both hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1-independent and HIF-1-dependent mechanisms. Cancer research 2006; 66: 3197–3204.
Nilsson MB, Zage PE, Zeng L, Xu L, Cascone T, Wu HK et al. Multiple receptor tyrosine kinases regulate HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in normoxia and hypoxia in neuroblastoma: implications for antiangiogenic mechanisms of multikinase inhibitors. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2938–2949.
Majumder PK, Febbo PG, Bikoff R, Berger R, Xue Q, McMahon LM et al. mTOR inhibition reverses Akt-dependent prostate intraepithelial neoplasia through regulation of apoptotic and HIF-1-dependent pathways. Nat Med 2004; 10: 594–601.
Verheul HM, Salumbides B, Van Erp K, Hammers H, Qian DZ, Sanni T et al. Combination strategy targeting the hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha with mammalian target of rapamycin and histone deacetylase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 3589–3597.
Liang D, Kong X, Sang N . Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on HIF-1. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 2006; 5: 2430–2435.
Mabjeesh NJ, Escuin D, LaVallee TM, Pribluda VS, Swartz GM, Johnson MS et al. 2ME2 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by disrupting microtubules and dysregulating HIF. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: 363–375.
Ricker JL, Chen Z, Yang XP, Pribluda VS, Swartz GM, Van Waes C . 2-methoxyestradiol inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha, tumor growth, and angiogenesis and augments paclitaxel efficacy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 8665–8673.
Escuin D, Kline ER, Giannakakou P . Both microtubule-stabilizing and microtubule-destabilizing drugs inhibit hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha accumulation and activity by disrupting microtubule function. Cancer Research 2005; 65: 9021–9028.
Lee K, Qian DZ, Rey S, Wei H, Liu JO, Semenza GL . Anthracycline chemotherapy inhibits HIF-1 transcriptional activity and tumor-induced mobilization of circulating angiogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 2353–2358.
Rapisarda A, Uranchimeg B, Scudiero DA, Selby M, Sausville EA, Shoemaker RH et al. Identification of small molecule inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 transcriptional activation pathway. Cancer research 2002; 62: 4316–4324.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, S., Diamond, P., Gronthos, S. et al. The emerging role of hypoxia, HIF-1 and HIF-2 in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 25, 1533–1542 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.122
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.122
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hypoxia induces chemoresistance to proteasome inhibitors through orchestrating deSUMOylation and ubiquitination of SRC-3 in multiple myeloma
Oncogene (2022)
-
Atypical induction of HIF-1α expression by pericellular Notch1 signaling suffices for the malignancy of glioblastoma multiforme cells
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
Crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress: a dynamic duo in multiple myeloma
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
Der Eisenstoffwechsel und seine Bedeutung für das Höhentraining
German Journal of Exercise and Sport Research (2021)
-
A SUMOylation-dependent HIF-1α/CLDN6 negative feedback mitigates hypoxia-induced breast cancer metastasis
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2020)