Abstract
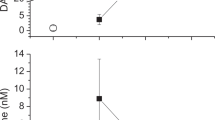
Concentrations of plasma arginine vasopressin (AVP) were studied in patients receiving chemotherapy. Of the 18 patients studied, nine experienced nausea and vomiting and the remaining nine were nonvomiters who suffered at worst mild nausea. Plasma AVP in the non-vomiting group remained within the normal range (0.5-1.5 pmol 1(-1] throughout the sampling period. However, patients who vomited showed (with one exception) substantial rises in AVP ranging from 4 to 129-fold. Plasma AVP concentrations were outside the normal range in vomiters and were higher than in non-vomiting patients at 3 h (P less than 0.05) and 5h (P less than 0.01) after chemotherapy. One patient was sampled during consecutive treatment courses, once as a vomiter and once as a non-vomiter; results demonstrated a 16-fold rise in AVP as a vomiter and no rise as a non-vomiter. Significant changes in plasma AVP levels were also observed in patients who suffered moderate or severe nausea compared to those who had mild or no nausea (P less than 0.05). Plasma AVP may prove to be a good objective marker for nausea in future anti-emetic trials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edwards, C., Carmichael, J., Baylis, P. et al. Arginine vasopressin – a mediator of chemotherapy induced emesis?. Br J Cancer 59, 467–470 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1989.96
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1989.96
This article is cited by
-
The role of the parasympathetic nervous system in visually induced motion sickness: systematic review and meta-analysis
Experimental Brain Research (2014)
-
Acupuncture for functional gastrointestinal disorders
Journal of Gastroenterology (2006)