Abstract
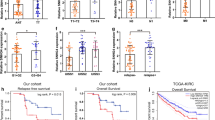
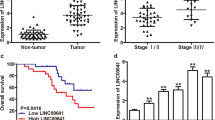
Although long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are known to play an important role in cell regulation in several cancers, the regulatory mechanisms in renal carcinoma cells remain unclear. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR), an lncRNA, coordinates with chromatin-modifying enzymes to regulate gene silencing. HOTAIR is over-expressed in several types of carcinoma cells. Thus, we hypothesised that lncRNA HOTAIR is crucial for cell proliferation and invasion and that its knockdown induces apoptosis in renal carcinoma cells. lncRNA HOTAIR expression was found to be elevated in renal carcinoma cells. Additionally, lncRNA HOTAIR knockdown by RNA interference with siRNA was found to significantly affect the cell cycle in the G0/G1 phase and weaken the abilities of cell proliferation and invasion in vitro. Xenograft experiments confirmed that the growth of xenograft tumours formed by renal carcinoma cells was suppressed after silencing lncRNA HOTAIR expression. Moreover, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays revealed that knockdown of lncRNA HOTAIR led to the weakening of the recruitment and binding abilities of EZH2 and H3K27me3 locus with lncRNA HOTAIR. Furthermore, the cell cycle-related gene locus was in an active transcriptional state by the silencing of lncRNA HOTAIR expression and modulation of covalent histones.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang C, Yu C, Yang F, Yang G: Diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for renal cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol 2014.
Zhang J, Zhang P, Wang L, Piao HL, Ma L. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in carcinogenesis and metastasis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014;46:1–5.
Bhan A, Hussain I, Ansari KI, Kasiri S, Bashyal A, Mandal SS. Antisense transcript long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) HOTAIR is transcriptionally induced by estradiol. J Mol Biol. 2013;425:3707–22.
Yang F, Zhang L, Huo XS, Yuan JH, Xu D, Yuan SX, et al. Long noncoding RNA high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma facilitates tumor growth through enhancer of zeste homolog 2 in humans. Hepatology. 2011;54:1679–89.
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N, Wang JK, Lan F, et al. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science. 2010;329:689–93.
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings HM, Wong DJ, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature. 2010;464:1071–6.
Sun L, Fang J. Writer meets eraser in hotair. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011;43:1–3.
Kim K, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Johnson G, Frank J, Burghardt R, et al. Hotair is a negative prognostic factor and exhibits pro-oncogenic activity in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 2012;32:1616–25.
Endo H, Shiroki T, Nakagawa T, Yokoyama M, Tamai K, Yamanami H, et al. Enhanced expression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated with the development of gastric cancer. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e77070.
Wan Y, Chang HY. HOTAIR: Flight of noncoding RNAs in cancer metastasis. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:3391–2.
Lv XB, Lian GY, Wang HR, Song E, Yao H, Wang MH. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR is a prognostic marker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression and survival. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e63516.
Liu T, Zou G, Gao Y, Zhao X, Wang H, Huang Q, et al. High efficiency of reprogramming cd34(+) cells derived from human amniotic fluid into induced pluripotent stem cells with oct4. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21:2322–32.
Cheng W, Liu T, Wan X, Gao Y, Wang H. MicroRNA-199a targets cd44 to suppress the tumorigenicity and multidrug resistance of ovarian cancer-initiating cells. FEBS J. 2012;279:2047–59.
Qin W, Ren Q, Liu T, Huang Y, Wang J. MicroRNA-155 is a novel suppressor of ovarian cancer-initiating cells that targets cldn1. FEBS Lett. 2013;587:1434–9.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81202811). The project was funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (no. 2014M550250) and the Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau Fund (no. 20124320) to Te Liu.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Liu, J., Zheng, Y. et al. Suppressed expression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits proliferation and tumourigenicity of renal carcinoma cells. Tumor Biol. 35, 11887–11894 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2453-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2453-4