Abstract
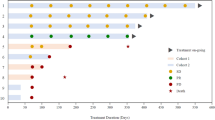
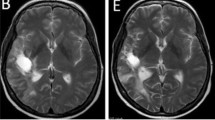
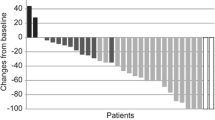
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are commonly observed in Glioblastoma (GBM) and have long posed as a target for new therapies. Trials involving erlotinib have shown mixed results, likely owing to a mechanism of the mutation that may instead favor other EGFR inhibitors, such as lapatinib. We aimed to determine whether or not pulse high-dose lapatinib was a safe and tolerable regimen in addition to standard therapy. We recruited adult patients with newly-diagnosed GBM who had Karnofsky Performance Status ≥60, normal baseline hematological, hepatic, and renal function tests, and no prior history of radiation or treatment with EGFR inhibitor. Lapatinib was administered at 2500 mg twice daily for two consecutive days per week on a weekly basis throughout concomitant and adjuvant standard therapy. The primary endpoints were tolerability and safety. 12 patients were enrolled in this study over 2 years. Of the non-hematological adverse events, there were 2 grade 3 events, fatigue and post-radiation cystic brain necrosis. The most common adverse events in general were fatigue, rashes, and diarrhea. Of the hematological adverse events, there were 13 grade 3 events, all of which were due to lymphopenia and affected 6 of 12 patients. Pulse high-dose lapatinib in addition to standard therapy for newly-diagnosed GBM is a tolerable and safe regimen, but higher rates of lymphopenia should be noted. However, further investigations will be required to evaluate the efficacy of this combination for the treatments of GBM.
Trial registration ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01591577.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quinn T, Ostrom HG, Fulop J, Liu M, Blanda R, Kromer C, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2015) CBTRUS Statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012. Neuro Oncol 17:iv1–iv62
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Cloughesy TF, Lassman AB (2017) NovoTTF: where to go from here? Neuro-oncol 19:605–608
Brennan CW, Verhaak RG, McKenna A et al (2013) The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 155:462–477
Barker FG 2nd, Simmons ML, Chang SM et al (2001) EGFR overexpression and radiation response in glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51:410–418
Mukherjee B, McEllin B, Camacho CV et al (2009) EGFRvIII and DNA double-strand break repair: a molecular mechanism for radioresistance in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 69:4252–4259
Nagane M, Coufal F, Lin H, Bogler O, Cavenee WK, Huang HJ (1996) A common mutant epidermal growth factor receptor confers enhanced tumorigenicity on human glioblastoma cells by increasing proliferation and reducing apoptosis. Cancer Res 56:5079–5086
Shinojima N, Tada K, Shiraishi S et al (2003) Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 63:6962–6970
Brown PD, Krishnan S, Sarkaria JN et al (2008) Phase I/II trial of erlotinib and temozolomide with radiation therapy in the treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme: North Central Cancer Treatment Group Study N0177. J Clin Oncol 26:5603–5609
Prados MD, Chang SM, Butowski N et al (2009) Phase II study of erlotinib plus temozolomide during and after radiation therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme or gliosarcoma. J Clin Oncol 27:579–584
Peereboom DM, Shepard DR, Ahluwalia MS et al (2010) Phase II trial of erlotinib with temozolomide and radiation in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 98:93–99
Raizer JJ, Abrey LE, Lassman AB et al (2010) A phase II trial of erlotinib in patients with recurrent malignant gliomas and nonprogressive glioblastoma multiforme postradiation therapy. Neuro-oncol 12:95–103
Vivanco I, Robins HI, Rohle D et al (2012) Differential sensitivity of glioma- versus lung cancer-specific EGFR mutations to EGFR kinase inhibitors. Cancer Discov 2:458–471
Chien AJ, Illi JA, Ko AH et al (2009) A phase I study of a 2-day lapatinib chemosensitization pulse preceding nanoparticle albumin-bound Paclitaxel for advanced solid malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 15:5569–5575
Levin VA, Crafts DC, Norman DM, Hoffer PB, Spire JP, Wilson CB (1977) Criteria for evaluating patients undergoing chemotherapy for malignant brain tumors. J Neurosurg 47:329–335
Institute NC (2009). Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v4.0. NIH publication # 09-7473
Reference PD (2015) 2016 Physicians’ Desk Reference.PDR Network, LLC, Montvale
Gilbert MR, Wang M, Aldape KD et al (2013) Dose-dense temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a randomized phase III clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 31:4085–4091
Karavasilis V, Kotoula V, Pentheroudakis G et al (2013) A phase I study of temozolomide and lapatinib combination in patients with recurrent high-grade gliomas. J Neurol 260:1469–1480
Funding
Novartis (previously Glaxo-Smith Kline) partially supported this pilot study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not declare any conflicts of interest related to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, A., Faiq, N., Green, S. et al. Report of safety of pulse dosing of lapatinib with temozolomide and radiation therapy for newly-diagnosed glioblastoma in a pilot phase II study. J Neurooncol 134, 357–362 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2533-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2533-6