Abstract
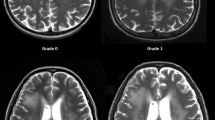
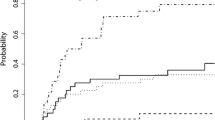
Brain metastases (BM) develop in 10–30 % of patients. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) was shown to improve local control, and performance status, in certain cohorts of brain metastasis patients. The cumulative neurocognitive effect of numerous SRS sessions remains unknown. Leukoencephalopathy is significant diffuse white matter changes and it usually implies a neurocognitive decline. We report patients with BM who survived >2 years after SRS. Clinical and treatment parameters were analyzed for development of leukoencephalopathy. Multiple parameters as well as leukoencephalopathy grade changes were recorded. The median clinical and radiological follow-up was 42 and 41 months (range 24–115 and 24–115) respectively. The cohort included 92 patients and 704 lesions. The most common malignancies were non-small cell lung carcinoma (44.5 % n = 41), breast adenocarcinoma (23.9 %, n = 22) and melanoma (16.3 %, n = 15). 27.6 % (n = 26) of patients underwent adjuvant WBRT. At last follow up, local tumor control was achieved in 76.3 % (n = 61) of patients and 71.8 % (n = 461) of lesions. Overall prevalence of leukoencephalopathy was 42, 60, 73 and 84 % at 1, 2, 3, and 4 years after SRS. Moderate-severe leukoencephalopathy development was related to an integral dose to skull >3 Joules (p = 0.012) at any radiosurgical treatment and prior WBRT (p < 0.042). Leukoencephalopathy incidence was consistently higher in the WBRT + SRS group at each following year of survival from initial SRS. Long-term BM survivors treated with SRS are at progressive risk for developing leukoencephalopathy. Those with a higher BM burden, higher integral SRS dose to the skull, and treatment with WBRT are at increased risk of leukoencephalopathy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nayak L, Lee EQ, Wen PY (2012) Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep 14:48–54
Patel KR, Prabhu RS, Kandula S, Oliver DE, Kim S, Hadjipanayis C et al (2014) Intracranial control and radiographic changes with adjuvant radiation therapy for resected brain metastases: whole brain radiotherapy versus stereotactic radiosurgery alone. J Neurooncol 120(3):657–663
Muacevic A, Wowra B, Siefert A, Tonn JC, Steiger HJ, Kreth FW (2008) Microsurgery plus whole brain irradiation versus Gamma Knife surgery alone for treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized controlled multicentre phase III trial. J Neurooncol 87:299–307
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG et al (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villà S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29(2):134–141
Aoyama H, Tago M, Kato N, Toyoda T, Kenjyo M, Hirota S et al (2007) Neurocognitive function of patients with brain metastasis who received either whole brain radiotherapy plus stereotactic radiosurgery or radiosurgery alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:1388–1395
Armstrong CL, Hunter JV, Ledakis GE, Cohen B, Tallent EM, Goldstein BH et al (2002) Late cognitive and radiographic changes related to radiotherapy: initial prospective findings. Neurology 59:40–48
Brown PD, Asher AL, Ballman KV, Farace E, Cerhan JH, Anderson K, et al (2015) NCCTG N0574 (Alliance): A phase III randomized trial of whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) in addition to radiosurgery (SRS) in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases. ASCO Annual Meeting, J Clin Oncol. 33 (suppl; abstr LBA4). http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/print/1985976
Correa DD, DeAngelis LM, Shi W, Shi W, Thaler H, Glass A et al (2004) Cognitive functions in survivors of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurology 62:548–555
Crossen JR, Garwood D, Glatstein E, Neuwelt EA (1994) Neurobehavioral sequelae of cranial Irradiation in adults: a review of radiation-induced encephalopathy. J Clin Oncol 12:627–642
Johannesen TB, Lien HH, Hole KH, Lote K (2003) Radiological and clinical assessment of long-Term braintumour survivors after radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 69:169–176
Monaco EA, Faraji AH, Berkowitz O, Parry PV, Hadelsberg U, Kano H et al (2013) Leukoencephalopathy after whole-brain radiation therapy plus radiosurgery versus radiosurgery alone for metastatic lung cancer. Cancer 119:226–232
Tsuruda JS, Kortman KE, Bradley WG, Wheeler DC, Van Dalsem W, Bradley TP et al (1987) Radiation effects on cerebral white matter: Mr evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 149:165–171
Dincoglan F, Sager O, Gamsiz H, Uysal B, Demiral S, Oysul K et al (2014) Management of patients with ≥ 4 brain metastases using stereotactic radiosurgery boost after whole brain irradiation. Tumori 100(3):302–306
Raldow AC, Chiang VL, Knisely JP, Yu JB (2013) Survival and intracranial control of patients With 5 or more brain metastases treated with gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery. Am J Clin Oncol 36:486–490
Xu Z, Elsharkawy M, Schlesinger D, Sheehan J (2013) Gamma knife radiosurgery for resectable brain metastasis. World Neurosurg 80(3–4):351–358
Stokes TB, Niranjan A, Kano H et al (2015) White matter changes in breast cancer brain metastases patients who undergo radiosurgery alone compared to whole brain radiation therapy plus radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 121(3):583–590
Snell JW, Sheehan J, Stroila M, Steiner L (2006) Assessment of imaging studies used with radiosurgery: a volumetric algorithm and an estimation of its error. Technical note. J Neurosurg 104(1):157–162
Oertel-Knöchel V, Reinke B, Alves G, Jurcoane A, Wenzler S, Prvulovic D et al (2014) Frontal white matter alterations are associated with executive cognitive function in euthymic bipolar patients. J Affect Disord 155:223–233
Griebe M, Forster A, Wessa M, Rossmanith C, Bäzner H, Sauer T et al (2011) Loss of callosal fibre integrity in healthy elderly With age-related white matter changes. J Neurol 258:1451–1459
Nakazawa H, Komori M, Mori Y, Hagiwara M, Shibamoto Y, Tsugawa T et al (2014) Effect of skull contours on dose calculations in gamma knife perfexion stereotactic radiosurgery. J Appl Clin Med Phys 15:4603
Tourbah A, Deschamps R, Stievenart JL, Lopez A, Iba-Zizen MT, Lyon-Caen O et al (1996) Magnetic resonance imaging using flair pulse sequence in white matter diseases. J Neuroradiol 23:217–222
Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA (1987) MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 t in alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. Am J Roentgenol 149:351–356
Fujii O, Tsujino K, Soejima T, Yoden E, Ichimiya Y, Sugimura K (2006) White matter changes on magnetic resonance imaging following whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases. Radiat Med 24:345–350
Huang AJ, Huang KE, Page BR, Ayala-Peacock DN, Lucas JT Jr, Lesser GJ et al (2014) Risk factors for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in patients with brain metastases who have previously undergone stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 120(1):163–169
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 15(4):387–395
Sabsevitz DS, Bovi JA, Leo PD, Laviolette PS, Rand SD, Mueller WM et al (2013) The role of pre-treatment white matter abnormalities in developing white matter changes following whole brain radiation: a volumetric study. J Neurooncol 114(3):291–297
Nazem-Zadeh MR, Chapman CH, Lawrence TL, Tsien CI, Cao Y (2012) Radiation therapy effects on white matter fiber tracts of the limbic circuit. Med Phys 39(9):5603–5613
Fouladi M, Chintagumpala M, Laningham FH, Ashley D, Kellie SJ, Langston JW et al (2004) White matter lesions detected by magnetic resonance imaging after radiotherapy and high-dose chemotherapy in children with medulloblastoma or primitive neuroectodermal tumor. J Clin Oncol 22(22):4551–4560
Kim SE, Lee JH, Chung HK, Lim SM, Lee HW (2014) Alterations in white matter microstructures and cognitive dysfunctions in benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Eur J Neurol 21(5):708–717
Bhatnagar AK, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2006) Stereotactic radio-surgery for four or more intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64(3):898–903
Likhacheva A, Pinnix CC, Parikh NR, Allen PK, McAleer MF, Chiu MS et al (2013) Predictors of survival in contemporary practice after initial radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85(3):656–661
Baschnagel AM, Meyer KD, Chen PY, Krauss DJ, Olson RE, Pieper DR et al (2013) Tumor volume as a predictor of survival and local control in patients with brain metastases treated with gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 119(5):1139–1144
Tofilon PJ, Fike JR (2000) The radioresponse of the central nervous system: a dynamic process. Radiat Res 153:357–370
Chuba PJ, Aronin P, Bhambhani K, Eichenhorn M, Zamarano L, Cianci P et al (1997) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for radiation-induced brain injury in children. Cancer 80:2005–2012
Coderre JA, Morris GM, Micca PL, Hopewell JW, Verhagen I, Kleiboer BJ et al (2006) Late effects of radiation on the central nervous system: role of vascular endothelial damage and glial stem cell survival. Radiat Res 166:495–503
Hulshof MC, Stark NM, van der Kleij A, Sminia P, Smeding HM, Gonzalez Gonzalez D (2002) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for cognitive disorders after irradiation of the brain. Strahlentherapie Onkol 178(4):192–198
Szerlip N, Rutter C, Ram N, Yovino S, Kwok Y, Maggio W et al (2011) Factors impacting volumetric white matter changes following whole brain radiation therapy. J Neurooncol 103:111–119
Brown PD, Pugh S, Laack NN, Wefel JS, Khuntia D, Meyers C et al (2013) Memantine for the prevention of cognitive dysfunction in patients receiving whole-brain radiotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, Placebo controlled trial. Neurooncology 15:1429–1437
Meyers CA, Weitzner MA, Valentine AD, Levin VA (1998) Methylphenidate therapy improves cognition, mood, and function of brain tumor patients. J Clin Oncol 16:2522–2527
Ghia A, Tome WA, Thomas S, Cannon G, Khuntia D, Kuo JS et al (2007) Distribution of brain metastases in relation to the hippocampus: implications for neurocognitive functional preservation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:971–977
Trifiletti DM, Xu Z, Lee CC, Schlesinger D, Larner JM, Sheehan JP (2015) Leukoencephalopathy following Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases: IJROBP
Acknowledgments
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no personal or institutional financial interest in drugs or materials in relation to this paper.
Disclosure
None.
Sources of funding
David Schlesinger receives research funding from Elekta Instruments, AB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen-Inbar, O., Melmer, P., Lee, Cc. et al. Leukoencephalopathy in long term brain metastases survivors treated with radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 126, 289–298 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1962-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1962-3