Abstract
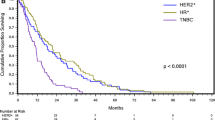
Leptomeningeal disease (LMD) occurs in 5 % of breast cancer patients. The aim of this study was to identify risk factors related to survival and time to development of LMD in breast cancer patients. A retrospective analysis of breast cancer patients with LMD, evaluated in MDACC between 1995 and 2011. 103 patients with diagnosis of breast cancer and LMD were identified (one male). The median age at LMD diagnosis was 49.2 years. 78.2 % had invasive ductal carcinoma. Hormone receptors (HRs) were positive in 55.3 % of patients, 47.4 % were human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive and 22.8 % were triple negative. 52 % of the patients were treated with WBRT, 19 % with spinal radiation, 36 % with systemic chemotherapy and 55 % with intrathecal chemotherapy. Estimated median overall survival from time of breast cancer diagnosis was 3.66 years. Median survival from time of LMD diagnosis was 4.2 months. Time from breast cancer diagnosis to LMD was 2.48 years. In multivariate analysis, HR status and stage at diagnosis were significantly associated with time to LMD diagnosis (p < 0.05). In triple negative patients, time to LMD was shorter. In patients who were HR positive, time to LMD was longer. Survival from LMD diagnosis was significantly associated with both treatment, as well as positive HR status (multivariate analysis p < 0.05). In conclusion LMD has dismal prognosis in breast cancer patients. HR status contributes to time to LMD diagnosis and survival from LMD diagnosis. The impact of treatment aimed at LMD cannot be ascertained in our retrospective study due to the inherent bias associated with the decision to treat.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 61(4):212
Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Cheang MC, Voduc D, Speers CH, Nielsen TO, Gelmon K (2010) Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol 28(20):3271–3277
Chamberlain MC (1998) Leptomeningeal metastases: a review of evaluation and treatment. J Neurooncol 37(3):271–284
Grewal J, Saria MG, Kesari S (2012) Novel approaches to treating leptomeningeal metastases. J Neurooncol 106(2):225–234
Kesari S, Batchelor TT (2003) Leptomeningeal metastases. Neurol Clin 21(1):25–66
Gleissner B, Chamberlain MC (2006) Neoplastic meningitis. Lancet Neurol 5:443–452
Chamberlain MC (2008) Neoplastic meningitis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 8:249–258
Grossman SA, Krabak MJ (1999) Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer Treat Rev 25(2):103–119
Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren JW et al (1983) Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Cancer 52:2349–2354
Lin NU, Bellon JR, Winer EP (2004) CNS metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(17):3608–3617
Slimane K, Andre F, Delaloge S, Dunant A, Perez A, Grenier J, Massard C, Spielmann M (2004) Risk factors for brain relapse in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 15(11):1640–1644
Hicks DG, Short SM, Prescott NL, Tarr SM, Coleman KA, Yoder BJ, Crowe JP, Choueiri TK, Dawson AE, Budd GT, Tubbs RR, Casey G (2006) Weil RJ Breast cancers with brain metastases are more likely to be estrogen receptor negative, express the basal cytokeratin CK5/6, and overexpress HER2 or EGFR. Am J Surg Pathol 30(9):1097–1104
de Azevedo CR, Cruz MR, Chinen LT, Peres SV, Peterlevitz MA, de Azevedo Pereira AE, Fanelli MF, Gimenes DL (2011) Meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer: prognostic factors and outcome. J Neurooncol 104(2):565–572
Boogerd W, Hart AAM, Sande JJV, Engelsman E (1991) Meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer. Cancer 15:1685–1695
Rudnicka H, Niwińska A, Murawska M (2007) Breast cancer leptomeningeal metastasis—the role of multimodality treatment. J Neurooncol 84:57–62
Jayson GC, Howell A, Harris M et al (1994) Carcinomatous meningitis in breast cancer: an aggressive disease variant. Cancer 74:3135–3141
Torrejón D, Oliveira M, Cortes J, Sanchez-Olle G, Gómez P, Bellet M, Saura C, Peg V, Rovira A, Di Cosimo S (2012) Implication of breast cancer phenotype for patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Breast. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2012
Gauthier H, Guilhaume MN, Bidard FC et al (2010) Survival of breast cancer patients with meningeal carcinomatosis. Ann Oncol. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq232
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Chao ST, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Suh J, Weil RJ, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JP, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M (2013) The effect of tumor subtype on the time from primary diagnosis to development of brain metastases and survival in patients with breast cancer. J Neurooncol. doi:10.1007/s11060-013-1083-9
Fleming ID, Cooper JS, Henson DE et al (eds) (1997) AJCC cancer staging manual, 5th edn. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 235(4785):177–182
Altundag K, Bondy ML, Mirza NQ, Kau SW, Broglio K, Hortobagyi GN, Rivera E (2007) Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic factors in 420 metastatic breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastasis. Cancer 110(12):2640–2647
Harstad L, Kenneth R, Groves MD (2008) Prognostic factors and outcomes in patients with leptomeningeal melanomatosis. Neuro Oncol 10(6):1010–1018
Conflict of interest
S. Yust-Katz, P. Garciarena, D. Liu, Y. Yuan, N. Ibrahim and M Penas-Prado: No conflict of interest. M. Groves: Research support: Merck, Celldex, Genentech, GSK, Honoraria: Merck, Sanofi-Aventis, Genentech. Advisory board: Sanofi-Aventis, Genentech. Speakers bureau: Enzon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yust-Katz, S., Garciarena, P., Liu, D. et al. Breast cancer and leptomeningeal disease (LMD): hormone receptor status influences time to development of LMD and survival from LMD diagnosis. J Neurooncol 114, 229–235 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1175-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1175-6