Abstract
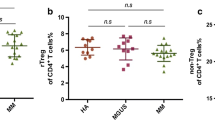
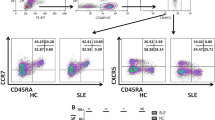
Immunological T cells and associated cytokines have been shown to be involved in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma (MM). However, the abnormal immune imbalance of T lymphocyte subsets on MM remains unknown. We investigate the proportions of T helper 1 (Th1)/Th2/Th17/T regulatory (Treg) cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by flow cytometry (FCM), and serum levels of relevant cytokines in MM patients and controls were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of T-bet, STAT6, RORgammat, and Foxp3 was measured by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The CD4+ Th1 and CD4+ Th17 cells in patients with MM were significantly higher than those in health controls as well as the expression of T-bet and RORgammat mRNA. Furthermore, serum levels of interferon gamma (IFN-γ), IL-6, and IL-17A in MM group were greatly increased and significantly associated with each other. Significant differences on Th cells, cytokines, and transcription factors were observed on MM patients. The imbalance of T lymphocyte subsets was thought to contribute to the pathogenesis and underlying mechanisms of MM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sedlarikova, L., et al. 2014. Cytokine profiles of multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Klinická Onkologie 27(1): 18–23.
Mehtap, O., et al. 2014. IL-21 and other serum proinflammatory cytokine levels in patients with multiple myeloma at diagnosis. Journal of Postgraduate Medicine 60(2): 141–4.
Song, X.N., et al. 2013. Expression levels of IL-27 and IL-17 in multiple myeloma patients: a higher ratio of IL-27:IL-17 in bone marrow was associated with a superior progression-free survival. Leukemia Research 37(9): 1094–9.
Abbas, A.K., K.M. Murphy, and A. Sher. 1996. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature 383(6603): 787–93.
Mosmann, T.R., and S. Sad. 1996. The expanding universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more. Immunology Today 17(3): 138–46.
Park, H., et al. 2005. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nature Immunology 6(11): 1133–41.
Bettelli, E., M. Oukka, and V.K. Kuchroo. 2007. T(H)-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nature Immunology 8(4): 345–50.
Komiyama, Y., et al. 2006. IL-17 plays an important role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Journal of Immunology 177(1): 566–73.
Sakaguchi, S., et al. 2006. Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune disease. Immunology Reviews 212: 8–27.
Ryba-Stanislawowska, M., et al. 2013. Loss of the balance between CD4(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells and CD4(+)IL17A(+) Th17 cells in patients with type 1 diabetes. Human Immunology 74(6): 701–7.
Boissier, M.C., et al. 2008. Shifting the imbalance from Th1/Th2 to Th17/treg: the changing rheumatoid arthritis paradigm. Joint, Bone, Spine 75(4): 373–5.
Cheng, X., et al. 2008. The Th17/Treg imbalance in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Clinical Immunology 127(1): 89–97.
Zhang, Y., et al. 2013. Function of peripheral blood Th17 cells in patients with multiple myeloma. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 21(5): 1187–9.
Jandus, C., et al. 2008. Increased numbers of circulating polyfunctional Th17 memory cells in patients with seronegative spondylarthritides. Arthritis and Rheumatism 58(8): 2307–17.
Elias, K.M., et al. 2008. Retinoic acid inhibits Th17 polarization and enhances FoxP3 expression through a Stat-3/Stat-5 independent signaling pathway. Blood 111(3): 1013–20.
Gavin, M.A., et al. 2007. Foxp3-dependent programme of regulatory T-cell differentiation. Nature 445(7129): 771–5.
Wang, X., et al. 2009. Expression of IL-23 and IL-17 and effect of IL-23 on IL-17 production in ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology International 29(11): 1343–7.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81301494).
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ping Feng and Ruhong Yan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, P., Yan, R., Dai, X. et al. The Alteration and Clinical Significance of Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg Cells in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Inflammation 38, 705–709 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9980-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9980-4