Abstract
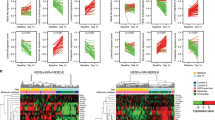
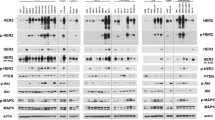
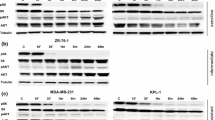
We studied resistance to endocrine and HER2-targeted therapies using a xenograft model of estrogen receptor positive (ER)/HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Here, we report a novel phenotype of drug resistance in this model. MCF7/HER2-18 xenografts were treated with endocrine therapy alone or in combination with lapatinib and trastuzumab (LT) to inhibit HER2. Archival tumor tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and with mucicarmine. RNA extracted from tumors at early time points and late after acquired resistance were analyzed for mucin4 (MUC4) expression by microarray and quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR. Protein expression of the MUC4, ER, and HER2 signaling pathways was measured by immunohistochemistry and western blotting. The combination of the potent anti-HER2 regimen LT with either tamoxifen (Tam + LT) or estrogen deprivation (ED + LT) can cause complete eradication of ER-positive/HER2-overexpressing tumors in mice. Tumors developing resistance to this combination, as well as those acquiring resistance to endocrine therapy alone, exhibited a distinct histological and molecular phenotype—a striking increase in mucin-filled vacuoles and upregulation of several mucins including MUC4. At the onset of resistance, MUC4 mRNA and protein were increased. These tumors also showed upregulation and reactivation of HER2 signaling, while losing ER protein and the estrogen-regulated gene progesterone receptor. Mucins are upregulated in a preclinical model of ER-positive/HER2-overexpressing breast cancer as resistance develops to the combination of endocrine and anti-HER2 therapy. These mucin-rich tumors reactivate the HER2 pathway and shift their molecular phenotype to become more ER-negative/HER2-positive.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arpino G, Gutierrez C, Weiss H, Rimawi M, Massarweh S, Bharwani L, De Placido S, Osborne CK, Schiff R (2007) Treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-overexpressing breast cancer xenografts with multiagent HER-targeted therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 99(9):694–705. doi:10.1093/jnci/djk151
Arpino G, Wiechmann L, Osborne CK, Schiff R (2008) Crosstalk between the estrogen receptor and the HER tyrosine kinase receptor family: molecular mechanism and clinical implications for endocrine therapy resistance. Endocr Rev 29(2):217–233. doi:10.1210/er.2006-0045
Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Creighton CJ, Qin L, Tsimelzon A, Huang S, Weiss H, Rimawi M, Schiff R (2008) Tamoxifen resistance in breast tumors is driven by growth factor receptor signaling with repression of classic estrogen receptor genomic function. Cancer Res 68(3):826–833. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2707
Britton DJ, Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM, Barrow D, Giles M, McClelland RA, Gee JM, Nicholson RI (2006) Bidirectional cross talk between ERalpha and EGFR signalling pathways regulates tamoxifen-resistant growth. Breast Cancer Res Treat 96(2):131–146. doi:10.1007/s10549-005-9070-2
Knowlden JM, Hutcheson IR, Jones HE, Madden T, Gee JM, Harper ME, Barrow D, Wakeling AE, Nicholson RI (2003) Elevated levels of epidermal growth factor receptor/c-erbB2 heterodimers mediate an autocrine growth regulatory pathway in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 cells. Endocrinology 144(3):1032–1044
Leary AF, Drury S, Detre S, Pancholi S, Lykkesfeldt AE, Martin LA, Dowsett M, Johnston SR (2010) Lapatinib restores hormone sensitivity with differential effects on estrogen receptor signaling in cell models of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer with acquired endocrine resistance. Clin Cancer Res 16(5):1486–1497. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1764
Ellis MJ, Coop A, Singh B, Mauriac L, Llombert-Cussac A, Janicke F, Miller WR, Evans DB, Dugan M, Brady C, Quebe-Fehling E, Borgs M (2001) Letrozole is more effective neoadjuvant endocrine therapy than tamoxifen for ErbB-1- and/or ErbB-2-positive, estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer: evidence from a phase III randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 19(18):3808–3816
Johnston S, Pippen J Jr, Pivot X, Lichinitser M, Sadeghi S, Dieras V, Gomez HL, Romieu G, Manikhas A, Kennedy MJ, Press MF, Maltzman J, Florance A, O’Rourke L, Oliva C, Stein S, Pegram M (2009) Lapatinib combined with letrozole versus letrozole and placebo as first-line therapy for postmenopausal hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(33):5538–5546. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.23.3734
Kaufman B, Mackey JR, Clemens MR, Bapsy PP, Vaid A, Wardley A, Tjulandin S, Jahn M, Lehle M, Feyereislova A, Revil C, Jones A (2009) Trastuzumab plus anastrozole versus anastrozole alone for the treatment of postmenopausal women with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive, hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: results from the randomized phase III TAnDEM study. J Clin Oncol 27(33):5529–5537. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.6847
Osborne CK, Neven P, Dirix LY, Mackey JR, Robert J, Underhill C, Schiff R, Gutierrez C, Migliaccio I, Anagnostou VK, Rimm DL, Magill P, Sellers M (2011) Gefitinib or placebo in combination with tamoxifen in patients with hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: a randomized phase II study. Clin Cancer Res 17(5):1147–1159. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1869
Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Jiang S, Wakeling AE, Rimawi M, Mohsin SK, Hilsenbeck S, Schiff R (2006) Mechanisms of tumor regression and resistance to estrogen deprivation and fulvestrant in a model of estrogen receptor-positive, HER-2/neu-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res 66(16):8266–8273. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4045
Rimawi MF, Wiechmann LS, Wang YC, Huang C, Migliaccio I, Wu MF, Gutierrez C, Hilsenbeck SG, Arpino G, Massarweh S, Ward R, Soliz R, Osborne CK, Schiff R (2011) Reduced dose and intermittent treatment with lapatinib and trastuzumab for potent blockade of the HER pathway in HER-2/neu-overexpressing breast tumor xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 17:1351–1361
Benz CC, Scott GK, Sarup JC, Johnson RM, Tripathy D, Coronado E, Shepard HM, Osborne CK (1992) Estrogen-dependent, tamoxifen-resistant tumorigenic growth of MCF-7 cells transfected with HER2/neu. Breast Cancer Res Treat 24(2):85–95
Moniaux N, Varshney GC, Chauhan SC, Copin MC, Jain M, Wittel UA, Andrianifahanana M, Aubert JP, Batra SK (2004) Generation and characterization of anti-MUC4 monoclonal antibodies reactive with normal and cancer cells in humans. J Histochem Cytochem 52(2):253–261
Creighton CJ, Massarweh S, Huang S, Tsimelzon A, Hilsenbeck SG, Osborne CK, Shou J, Malorni L, Schiff R (2008) Development of resistance to targeted therapies transforms the clinically associated molecular profile subtype of breast tumor xenografts. Cancer Res 68(18):7493–7501. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1404
Saldanha AJ (2004) Java Treeview—extensible visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics 20(17):3246–3248. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bth349bth349
Hammerich-Hille S, Kaipparettu BA, Tsimelzon A, Creighton CJ, Jiang S, Polo JM, Melnick A, Meyer R, Oesterreich S (2010) SAFB1 mediates repression of immune regulators and apoptotic genes in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 285(6):3608–3616. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.066431
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Tibes R, Qiu Y, Lu Y, Hennessy B, Andreeff M, Mills GB, Kornblau SM (2006) Reverse phase protein array: validation of a novel proteomic technology and utility for analysis of primary leukemia specimens and hematopoietic stem cells. Mol Cancer Ther 5(10):2512–2521. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0334
Shapiro SS, Wilk MB (1965) An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 52(3–4):591–611
Mann HB, Whitney DR (1947) On a test of whether one of two random variables is stochastically larger than the other. Ann Math Stat 18(1):50–60
Team RDC (2010) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Steinbrecher JS, Silverberg SG (1976) Signet-ring cell carcinoma of the breast. The mucinous variant of infiltrating lobular carcinoma? Cancer 37(2):828–840
Chaturvedi P, Singh AP, Chakraborty S, Chauhan SC, Bafna S, Meza JL, Singh PK, Hollingsworth MA, Mehta PP, Batra SK (2008) MUC4 mucin interacts with and stabilizes the HER2 oncoprotein in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 68(7):2065–2070. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6041
Carraway KL, Perez A, Idris N, Jepson S, Arango M, Komatsu M, Haq B, Price-Schiavi SA, Zhang J, Carraway CA (2002) Muc4/sialomucin complex, the intramembrane ErbB2 ligand, in cancer and epithelia: to protect and to survive. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 71:149–185
Hollingsworth MA, Swanson BJ (2004) Mucins in cancer: protection and control of the cell surface. Nat Rev Cancer 4(1):45–60. doi:10.1038/nrc1251nrc1251
Karg A, Dinc ZA, Basok O, Ucvet A (2006) MUC4 expression and its relation to ErbB2 expression, apoptosis, proliferation, differentiation, and tumor stage in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Pathol Res Pract 202(8):577–583. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2006.04.002
Kwon KY, Ro JY, Singhal N, Killen DE, Sienko A, Allen TC, Zander DS, Barrios R, Haque A, Cagle PT (2007) MUC4 expression in non-small cell lung carcinomas: relationship to tumor histology and patient survival. Arch Pathol Lab Med 131(4):593–598
Tamada S, Shibahara H, Higashi M, Goto M, Batra SK, Imai K, Yonezawa S (2006) MUC4 is a novel prognostic factor of extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 12(14 Pt 1):4257–4264. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2814
Tsutsumida H, Goto M, Kitajima S, Kubota I, Hirotsu Y, Wakimoto J, Batra SK, Imai K, Yonezawa S (2007) MUC4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in small-sized lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 55(2):195–203. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.10.013
Chauhan SC, Singh AP, Ruiz F, Johansson SL, Jain M, Smith LM, Moniaux N, Batra SK (2006) Aberrant expression of MUC4 in ovarian carcinoma: diagnostic significance alone and in combination with MUC1 and MUC16 (CA125). Mod Pathol 19(10):1386–1394. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800646
Munro EG, Jain M, Oliva E, Kamal N, Lele SM, Lynch MP, Guo L, Fu K, Sharma P, Remmenga S, Growdon WB, Davis JS, Rueda BR, Batra SK (2009) Upregulation of MUC4 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma: pathologic significance. Int J Gynecol Pathol 28(2):127–133. doi:10.1097/PGP.0b013e318184f3e0
Singh AP, Chauhan SC, Bafna S, Johansson SL, Smith LM, Moniaux N, Lin MF, Batra SK (2006) Aberrant expression of transmembrane mucins, MUC1 and MUC4, in human prostate carcinomas. Prostate 66(4):421–429. doi:10.1002/pros.20372
Miyahara N, Shoda J, Ishige K, Kawamoto T, Ueda T, Taki R, Ohkohchi N, Hyodo I, Thomas MB, Krishnamurthy S, Carraway KL, Irimura T (2008) MUC4 interacts with ErbB2 in human gallbladder carcinoma: potential pathobiological implications. Eur J Cancer 44(7):1048–1056. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.03.007
Andrianifahanana M, Moniaux N, Schmied BM, Ringel J, Friess H, Hollingsworth MA, Buchler MW, Aubert JP, Batra SK (2001) Mucin (MUC) gene expression in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis: a potential role of MUC4 as a tumor marker of diagnostic significance. Clin Cancer Res 7(12):4033–4040
Workman HC, Miller JK, Ingalla EQ, Kaur RP, Yamamoto DI, Beckett LA, Young LJ, Cardiff RD, Borowsky AD, Carraway KL, Sweeney C, Carraway KL 3rd (2009) The membrane mucin MUC4 is elevated in breast tumor lymph node metastases relative to matched primary tumors and confers aggressive properties to breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 11(5):R70. doi:10.1186/bcr2364
Workman HC, Sweeney C, Carraway KL 3rd (2009) The membrane mucin Muc4 inhibits apoptosis induced by multiple insults via ErbB2-dependent and ErbB2-independent mechanisms. Cancer Res 69(7):2845–2852. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2089
Ramsauer VP, Pino V, Farooq A, Carothers Carraway CA, Salas PJ, Carraway KL (2006) Muc4–ErbB2 complex formation and signaling in polarized CACO-2 epithelial cells indicate that Muc4 acts as an unorthodox ligand for ErbB2. Mol Biol Cell 17(7):2931–2941. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-09-0895
Yokoyama A, Shi BH, Kawai T, Konishi H, Andoh R, Tachikawa H, Ihara S, Fukui Y (2007) Muc4 is required for activation of ErbB2 in signet ring carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 355(1):200–203. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.133
Carraway KL 3rd, Rossi EA, Komatsu M, Price-Schiavi SA, Huang D, Guy PM, Carvajal ME, Fregien N, Carraway CA, Carraway KL (1999) An intramembrane modulator of the ErbB2 receptor tyrosine kinase that potentiates neuregulin signaling. J Biol Chem 274(9):5263–5266
Funes M, Miller JK, Lai C, Carraway KL 3rd, Sweeney C (2006) The mucin Muc4 potentiates neuregulin signaling by increasing the cell-surface populations of ErbB2 and ErbB3. J Biol Chem 281(28):19310–19319. doi:10.1074/jbc.M603225200
Nagy P, Friedlander E, Tanner M, Kapanen AI, Carraway KL, Isola J, Jovin TM (2005) Decreased accessibility and lack of activation of ErbB2 in JIMT-1, a herceptin-resistant, MUC4-expressing breast cancer cell line. Cancer Res 65(2):473–482
Price-Schiavi SA, Jepson S, Li P, Arango M, Rudland PS, Yee L, Carraway KL (2002) Rat Muc4 (sialomucin complex) reduces binding of anti-ErbB2 antibodies to tumor cell surfaces, a potential mechanism for herceptin resistance. Int J Cancer 99(6):783–791. doi:10.1002/ijc.10410
Mejias-Luque R, Peiro S, Vincent A, Van Seuningen I, de Bolos C (2008) IL-6 induces MUC4 expression through gp130/STAT3 pathway in gastric cancer cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783(10):1728–1736. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.05.020
Andrianifahanana M, Singh AP, Nemos C, Ponnusamy MP, Moniaux N, Mehta PP, Varshney GC, Batra SK (2007) IFN-gamma-induced expression of MUC4 in pancreatic cancer cells is mediated by STAT-1 upregulation: a novel mechanism for IFN-gamma response. Oncogene 26(51):7251–7261. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210532
Andrianifahanana M, Agrawal A, Singh AP, Moniaux N, van Seuningen I, Aubert JP, Meza J, Batra SK (2005) Synergistic induction of the MUC4 mucin gene by interferon-gamma and retinoic acid in human pancreatic tumour cells involves a reprogramming of signalling pathways. Oncogene 24(40):6143–6154. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208756
Damera G, Xia B, Ancha HR, Sachdev GP (2006) IL-9 modulated MUC4 gene and glycoprotein expression in airway epithelial cells. Biosci Rep 26(1):55–67. doi:10.1007/s10540-006-9000-5
Damera G, Xia B, Sachdev GP (2006) IL-4 induced MUC4 enhancement in respiratory epithelial cells in vitro is mediated through JAK-3 selective signaling. Respir Res 7:39. doi:10.1186/1465-9921-7-39
Perez A, Barco R, Fernandez I, Price-Schiavi SA, Carraway KL (2003) PEA3 transactivates the Muc4/sialomucin complex promoter in mammary epithelial and tumor cells. J Biol Chem 278(38):36942–36952. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300264200M300264200
Guo S, Sonenshein GE (2004) Forkhead box transcription factor FOXO3a regulates estrogen receptor alpha expression and is repressed by the Her-2/neu/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 24(19):8681–8690. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.19.8681-8690.200424/19/8681
Creighton CJ, Fu X, Hennessy BT, Casa AJ, Zhang Y, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Lluch A, Gray JW, Brown PH, Hilsenbeck SG, Osborne CK, Mills GB, Lee AV, Schiff R (2010) Proteomic and transcriptomic profiling reveals a link between the PI3K pathway and lower estrogen-receptor (ER) levels and activity in ER+ breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 12(3):R40. doi:10.1186/bcr2594
Moniaux N, Chaturvedi P, Varshney GC, Meza JL, Rodriguez-Sierra JF, Aubert JP, Batra SK (2007) Human MUC4 mucin induces ultra-structural changes and tumorigenicity in pancreatic cancer cells. Br J Cancer 97(3):345–357. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603868
Ponnusamy MP, Singh AP, Jain M, Chakraborty S, Moniaux N, Batra SK (2008) MUC4 activates HER2 signalling and enhances the motility of human ovarian cancer cells. Br J Cancer 99(3):520–526. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604517
Ponnusamy MP, Lakshmanan I, Jain M, Das S, Chakraborty S, Dey P, Batra SK (2010) MUC4 mucin-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition: a novel mechanism for metastasis of human ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.309
Shou J, Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Wakeling AE, Ali S, Weiss H, Schiff R (2004) Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96(12):926–935
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Rena Mao and the Baylor Breast Center Pathology Core, Robin Ward and Maria Fernanda Prigge for technical assistance, Dr. Susan Hilsenbeck for advice on statistical analysis, Dr. Gary Chamness for help with manuscript writing, and Dr. Kermit Carraway for scientific discussion. This study was supported by DOD Grant W81XWH-08-1-0264 (to A.C.C.) and NIH SPORE Grant P50CA058183 and Cancer Center Grant P30CA125123, the EIF/Lee Jeans Breast Cancer Research Program, Breast Cancer Research Foundation and Stand Up 2 Cancer (to C.K.O. and R.S.).
Disclosures
The experiments described in this study comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed. The authors declare that they have no relevant conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, A.C., Migliaccio, I., Rimawi, M. et al. Upregulation of mucin4 in ER-positive/HER2-overexpressing breast cancer xenografts with acquired resistance to endocrine and HER2-targeted therapies. Breast Cancer Res Treat 134, 583–593 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2082-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2082-9