Abstract
Objectives
Palonosetron is a novel 5-hydroxytryptamine3 (5 HT3) receptor antagonist, which has been shown to be superior to first generation 5 HT3 receptor antagonists regarding the prevention of acute, delayed and overall chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. First generation 5 HT3 receptor antagonists may induce electrocardiographic changes of heart rate and repolarization. The acute cardiac effect of palonosteron is unknown. The purpose of this study is to determine acute effects of palonosetron on electrocardiographic (ECG) parameters in cancer patients.
Materials and methods
The study had a prospective design. Seventy-six cancer patients with normal cardiac function who received palonosetron for prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting were enrolled. Standard 12-lead ECG recordings were performed at baseline and 30 min after palonosetron administration. P wave durations and corrected QT intervals were measured; P wave dispersion (Pd) and QTc dispersion were calculated.
Results
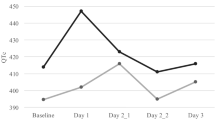
Median heart rate did not differ among 76 patients enrolled before and after palonosetron administration (p: 0.6). Systolic and diastolic blood pressures were not significantly different before and after palonosteron (p values 0.9 and 0.3, respectively). Although median QT min value was higher after palonosetron administration than before palonosetron administration, the difference was not statistically significant (p: 0.6).
Conclusion
Palonosetron seems to have no acute arrhythmogenic potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aapro M, Bourke JP (2003) Rapid intravenous administration of granisetron prior to chemotherapy is not arythmogenic: results of a pilot study. Eur J Cancer 39:927–931
O'Brien BJ, Rusthoven J, Rocchi a et al (1993) Impact of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting on patients' functional status and on costs: survey of five Canadian centers. Can Med Assoc J 149:296–302
Navari RM (2003) Pathogenesis-based treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting-two new agents. J Support Oncol 1:89–103
De Leon A (2006) Palonosetron (Aloxi): a second-generation 5-HT3 receptor antagonist for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Bayl Univ Med Cent Proc 19:413–416
Doherty KM (1999) Closing the gap in prophylactic antiemetic therapy: patient factors in calculating the emetogenic potential of chemotherapy. Clin J Oncol Nurs 3:113–119
Jantunen IT, Kataja VV, Muhonen TT, Parviainen T (1996) Effects of granisetron with doxorubicin or epirubicin on ECG intervals. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 37:502–504
Yavas O, Yazici M, Eren O, Boruban C, Artac M, Genc M (2008) The acute effect of tropisetron on ECG parameters in cancer patients. Support Care Cancer 16:1011–1015
Buyukavci M, Olgun Hi Ceviz N (2005) The effects of ondansetron ang granisetron on electrocardiography in children receiving chemotherapy for acute leukemia. Am J Clin Oncol 28:201–204
Navari RM, Koeller JM (2003) Electrocariographic and cardiovascular effects of the 5-hydroxitryptamine 3 receptor antagonists. Ann Pharmocother 37:1276–1286
Watanabe H, Hasegawa A, Shinozaki T et al (1995) Possible cardiac side effects of granisteron an entiemetic agent, in patients with bone and soft-tissue sarcomas receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 35:278–282
Kasinath NS, Malak O, Tetzlaff J (2003) Atrial fibriallation after ondansetron for the prevention and treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting a case report. Can J Anaesth 50:229–231
Audhuy B, Cappelaere P, Martin M et al (1996) A double-blind, randomized comparison of the antiemetic efficacy of two intravenous doses of dolasetron mesilate and granisetron in patients receiving high dose cisplatin chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer 32A(5):807–813
Ballard HS, Bottino G, Bottino J (1992) Ondansetron and chest pain. Lancet 340(8827):1107
Boike SC, Ilson B, Zariffa N et al (1997) Cardiovascular effects of i.v. granisetron at two administration rates and of ondansetron in healthy adults. Am J Health Syst Pharm 54(10):1172–1176
Hunt TL, Cramer M, Shah A et al (1995) A double-blind placebo-controlled, dose-ranging safety evaluation of single-dose intravenous dolasetron in healthy male volunteers. J Clin Pharmocol 35(7):705–712
Hesketh P, Navari R, Grote T et al (1996) Double-blind, randomized comparison of the antiemetic efficacy of intravenous dolasetron mesylate and intravenous ondansetron in the prevention of acute cisplatin-induced emesis in patients with cancer. Dolasetron Comparative Chemotherapy-induced Emesis Prevention Group. J Clin Oncol 14(8):2242–2249
Eisenberg P, Figueroa-Vadillo J, Zamora R, Charu V, Hajdenberg J, Cartmell A, Macciocchi A, Grunberg S (2003) Improved prevention of moderately emetogenic chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting with palonosetron, a pharmacologically novel 5-HT3 receptor antagonist: results of a phase III, single-dose trial versus dolasetron. Cancer 98:2473–2482
Gralla R, Lichinitser M, Van Der Vegt S, Sleeboom H, Mezger J, Peschel C, Tonini G, Labianca R, Macciocchi A, Aapro M (2003) Palonosetron improves prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting following moderately emetogenic chemotherapy: results of a double-blind randomized phase III trial comparing single doses of palonosetron with ondansetron. Ann Oncol 14:1570–1577
Morganroth J (2007) Cardiac repolarization and the safety of new drugs defined by electrocardiography. Clin Pharmacol Ther 81(1):108–113
Morganroth J (2001) Focus on issues in measuring and interpreting changes in the QTc interval duration. Eur Heart J 3:105–111
Morganroth J (2007) Evaluation of the effect on cardiac repolarization (QTc interval) of oncologic drugs. Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop 59:171–184
Kris MG, Grunberg SM, Gralla RJ et al (1994) Dose-ranging evaluation of the serotonin antagonist dolasetron mesylate in patients receiving high-dose cisplatin. J Clin Oncol 12:1045–1049
Lifsey DS, Gralla RJ, Clark RA, Kline RC (1993) Electrocardiographic changes with serotonin antagonist antiemetics:rate of occurrence and clinical relevance. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 12:463, abst 1611
Gialafos JE (1999) P-wave dispersion. Eur Heart J 20(4):317
Dilaveris PE, Gialafos EJ, Sideris SK, Theopistou AM, Andrikopoulos GK, Kyriakidis M, Gialafos JE et al (1998) Simple electrocardiographic markers for the prediction of paroxysmal idiopathic atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J 135:733–738
Dilaveris PE, Gialafos EJ, Andrikopoulos GK, Richter DJ, Papanikolaou V, Poralis K, Gialafos JE (2000) Clinical and electrocardiographic predictors of recurrent atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 23:352–358
Bitzen A, Sternickel K, Lewalter T, Schwab JO, Yang A, Schrickel JW, Linhart M et al (2007) Automatic p wave analysis over 24 hours in patients with paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 12:306–315
Bazzet HR (1920) An analysis of the time relations of electrocardiographs. Heart 7:353–370
Benedict CR, Arbogast R, Martin L, Patton L, Morrill B, Hahne W (1996) Single-blind study of the effects of intravenous dalasetron mesylate versus ondansetron on electrocardiographic parameters in normal volunteers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 28:53–59
Gray GW, McLellan TM, Ducharme MB (1996) Granisetron shows no pro-arrhythmic effect in normal subjects during or after exercise in a hot environment. Aviat Space Environ Med 67(8):759–761
Lofters WS, Pater JL, Zee B et al (1997) Phase III double-blind comparison of dolasetron mesylate and ondansetron and an evaluation of the additive role of dexamethasone in the prevention of acute and delayed nausea and vomiting due to moderately emetogenic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 15(8):2966–2973
Kuryshev YA, Brown AM, Wang L, Benedict CR, Rampe D (2000) Interactions of the 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 antagonist class of antiemetic drugs with human cardiac ion channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295(2):614–620
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yavas, C., Dogan, U., Yavas, G. et al. Acute effect of palonosetron on electrocardiographic parameters in cancer patients: a prospective study. Support Care Cancer 20, 2343–2347 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-011-1348-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-011-1348-9