Abstract
Background
Robotic rectal surgery is gaining in popularity. We aimed to define the learning curve of an experienced laparoscopic colorectal surgeon in performing robot-assisted rectal surgery. We hypothesized that there are multiple phases in this learning process.
Methods
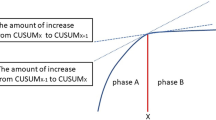
We performed a retrospective analysis. Consecutive patients who underwent robot-assisted rectal surgery between July 2007 and August 2011 were identified. Operating times were analyzed using the CUSUM (cumulative sum) technique. CUSUMs were model fitted as a fourth-order polynomial. χ2, Fisher’s exact, two independent samples t test, one-way ANOVA, Kruskal–Wallis, and Mann–Whitney tests were used. A p value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
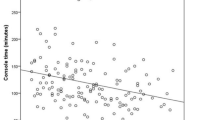
We identified 197 patients. The median (range) total operative, robot, console, and docking times (min) were 265 (145–515), 140 (59–367), 135 (50–360), and 5 (3–40), respectively. CUSUM analysis of docking time showed a learning curve of 35 cases. CUSUM analysis of total operative, robot, and console times demonstrated three phases. The first phase (35 patients) represented the initial learning curve. The second phase (93 patients) involved more challenging cases with increased operative time. The third phase (69 patients) represented the concluding phase in the learning curve. There was increased complexity of cases in the latter two phases. Of phase 1 patients, 45.7 % had tumors ≤7 cm from the anal verge compared to 64.2 % in phases 2 and 3 (p = 0.042). Of phase 1 patients, 2.9 % had neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy compared to 32.7 % of patients in phases 2 and 3 (p < 0.001). Splenic flexure was mobilized in 8.6 % of phase 1 patients compared to 56.8 % of patients in phases 2 and 3 (p < 0.001). Median blood loss was <50 ml in all three phases. The patients in phases 2 and 3 had a longer hospital stay compared to those in phase 1 (9 vs. 8 days, p = 0.002). There were no conversions.
Conclusion
At least three phases in the learning curve for robot-assisted rectal surgery are defined in our study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanly EJ, Marohn MR, Bachman SL, Talamini MA, Hacker SO, Howard RS, Schenkman NS (2004) Multiservice laparoscopic surgical training using the daVinci surgical system. Am J Surg 187:309–315
Bege T, Lelong B, Esterni B, Turrini O, Guiramand J, Francon D, Mokart D, Houvenaeghel G, Giovannini M, Delpero JR (2010) The learning curve for the laparoscopic approach to conservative mesorectal excision for rectal cancer: lessons drawn from a single institution’s experience. Ann Surg 251:249–253
Hellan M, Anderson C, Ellenhorn JD, Paz B, Pigazzi A (2007) Short-term outcomes after robotic-assisted total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 14:3168–3173
Bianchi PP, Ceriani C, Locatelli A, Spinoglio G, Zampino MG, Sonzogni A, Crosta C, Andreoni B (2010) Robotic versus laparoscopic total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer: a comparative analysis of oncological safety and short-term outcomes. Surg Endosc 24:2888–2894
Luca F, Cenciarelli S, Valvo M, Pozzi S, Faso FL, Ravizza D, Zampino G, Sonzogni A, Biffi R (2009) Full robotic left colon and rectal cancer resection: technique and early outcome. Ann Surg Oncol 16:1274–1278
D’Annibale A, Morpurgo E, Fiscon V, Trevisan P, Sovernigo G, Orsini C, Guidolin D (2004) Robotic and laparoscopic surgery for treatment of colorectal diseases. Dis Colon Rectum 47:2162–2168
Leong QM, Son DN, Cho JS, Baek SJ, Kwak JM, Amar AH, Kim SH (2011) Robot-assisted intersphincteric resection for low rectal cancer: technique and short-term outcome for 29 consecutive patients. Surg Endosc 25:2987–2992
Kwak JM, Kim SH, Kim J, Son DN, Baek SJ, Cho JS (2011) Robotic vs laparoscopic resection of rectal cancer: short-term outcomes of a case-control study. Dis Colon Rectum 54:151–156
Choi DJ, Kim SH, Lee PJ, Kim J, Woo SU (2009) Single-stage totally robotic dissection for rectal cancer surgery: technique and short-term outcome in 50 consecutive patients. Dis Colon Rectum 52:1824–1830
Novick RJ, Stitt LW (1999) The learning curve of an academic cardiac surgeon: use of the CUSUM method. J Card Surg 14:312–320
Van Rij AM, McDonald JR, Pettigrew RA, Putterill MJ, Reddy CK, Wright JJ (1995) CUSUM as an aid to early assessment of the surgical trainee. Br J Surg 82:1500–1503
Tekkis PP, Senagore AJ, Delaney CP, Fazio VW (2005) Evaluation of the learning curve in laparoscopic colorectal surgery: comparison of right-sided and left-sided resections. Ann Surg 242:83–91
Tekkis PP, Fazio VW, Lavery IC, Remzi FH, Senagore AJ, Wu JS, Strong SA, Poloneicki JD, Hull TL, Church JM (2005) Evaluation of the learning curve in ileal pouch-anal anastomosis surgery. Ann Surg 241:262–268
Bokhari MB, Patel CB, Ramos-Valadez DI, Ragupathi M, Haas EM (2011) Learning curve for robotic-assisted laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Surg Endosc 25:855–860
Buchs NC, Pugin F, Bucher P, Hagen ME, Chassot G, Koutny-Fong P, Morel P (2012) Learning curve for robot-assisted Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Endosc 26:1116–1121
Novick RJ, Fox SA, Kiaii BB, Stitt LW, Rayman R, Kodera K, Menkis AH, Boyd WD (2003) Analysis of the learning curve in telerobotic, beating heart coronary artery bypass grafting: a 90 patient experience. Ann Thorac Surg 76:749–753
Clavien PA, Barkun J, de Oliveira ML, Vauthey JN, Dindo D, Schulick RD, de Santibañes E, Pekolj J, Slankamenac K, Bassi C, Graf R, Vonlanthen R, Padbury R, Cameron JL, Makuuchi M (2009) The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: five-year experience. Ann Surg 250:187–196
Jayne DG, Thorpe HC, Copeland J, Quirke P, Brown JM, Guillou PJ (2010) Five-year follow-up of the Medical Research Council CLASICC trial of laparoscopically assisted versus open surgery for colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 97:1638–1645
Kang SB, Park JW, Jeong SY, Nam BH, Choi HS, Kim DW, Lim SB, Lee TG, Kim DY, Kim JS, Chang HJ, Lee HS, Kim SY, Jung KH, Hong YS, Kim JH, Sohn DK, Kim DH, Oh JH (2010) Open versus laparoscopic surgery for mid or low rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (COREAN trial): short-term outcomes of an open-label randomized controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 11:637–645
Laurent C, Leblanc F, Wütrich P, Scheffler M, Rullier E (2009) Laparoscopic versus open surgery for rectal cancer: long-term oncologic results. Ann Surg 250:54–61
Bretagnol F, Lelong B, Laurent C, Moutardier V, Rullier A, Monges G, Delpero JR, Rullier E (2005) The oncological safety of laparoscopic total mesorectal excision with sphincter preservation for rectal carcinoma. Surg Endosc 19:892–896
Spinoglio G, Summa M, Priora F, Quarati R, Testa S (2008) Robotic colorectal surgery: first 50 cases experience. Dis Colon Rectum 51:1627–1632
Chang L, Satava RM, Pellegrini CA, Sinanan MN (2003) Robotic surgery: identifying the learning curve through objective measurement of skill. Surg Endosc 17:1744–1748
Huang KH, Lan YT, Fang WL, Chen JH, Lo SS, Hsieh MC, Li AF, Chiou SH, Wu CW (2012) Initial experience of robotic gastrectomy and comparison with open and laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer. J Gastrointest Surg 16:1303–1310
Kandil EH, Noureldine SI, Yao L, Slakey DP (2012) Robotic transaxillary thyroidectomy: an examination of the first one hundred cases. J Am Coll Surg 214:558–564
Akmal Y, Baek JH, McKenzie S, Garcia-Aguilar J, Pigazzi A (2012) Robot-assisted total mesorectal excision: is there a learning curve? Surg Endosc 26:2471–2476
Voitk AJ, Tsao SG, Ignatius S (2001) The tail of the learning curve for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Am J Surg 182:250–253
Marusch F, Gastinger I, Schneider C, Scheidbach H, Konradt J, Bruch HP, Köhler L, Bärlehner E, Köckerling F; Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery Study Group (LCSSG) (2001) Experience as a factor influencing the indications for laparoscopic colorectal surgery and the results. Surg Endosc 15:116–120
Pigazzi A, Luca F, Patriti A, Valvo M, Ceccarelli G, Casciola L, Biffi R, Garcia-Aguilar J, Baek JH (2010) Multicentric study on robotic tumor-specific mesorectal excision for the treatment of rectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 17:1614–1620
Darzi A, Smith S, Taffinder N (1999) Assessing operative skill. Needs to become more objective. BMJ 318:887–888
Disclosures
Kevin Kaity Sng, Masayasu Hara, Jae-Won Shin, Byung-Eun Yoo, Kyung-Sook Yang, and Seon-Hahn Kim have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sng, K.K., Hara, M., Shin, JW. et al. The multiphasic learning curve for robot-assisted rectal surgery. Surg Endosc 27, 3297–3307 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-2909-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-2909-4