Abstract
Purpose
Icotinib is a new first-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors. A phase II study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of icotinib in combination with whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) in Chinese NSCLC patients with brain metastases (BMs); the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)/plasma concentrations of icotinib were also investigated.
Methods
Eligible patients had BMs from NSCLC, regardless of the EGFR status. Icotinib was administered at 125 mg orally 3 times/day until tumor progression or unacceptable toxicity, concurrently with WBRT (3.0 Gy per day, 5 days per week, to 30 Gy). CSF and plasma samples were collected simultaneously from 10 patients. Icotinib concentrations in the CSF and plasma were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry.
Results
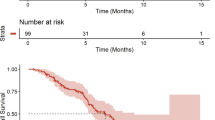
Twenty patients were enrolled. The median follow-up time was 20.0 months. The overall response rate was 80.0 %. The median progression-free survival time was 7.0 months (95 % CI 1.2–13.2 months), and the median survival time (MST) was 14.6 months (95 % CI 12.5–16.7 months). Of the 18 patients with known EGFR status, the MST was 22.0 months for those with an EGFR mutation and was 7.5 months for those with wild-type EGFR (P = 0.0001). The CSF concentration and penetration rate of icotinib were 11.6 ± 9.1 ng/mL and 1.4 ± 1.1 %, respectively. No patient experienced ≥grade 4 toxicity.
Conclusions
Icotinib was well tolerated in combination with WBRT and showed efficacy in patients with BMs from NSCLC. This clinical benefit was related to the presence of activating EGFR mutations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sørensen JB, Hansen HH, Hansen M, Dombernowsky P (1988) Brain metastases in adenocarcinoma of the lung: frequency, risk groups, and prognosis. J Clin Oncol 6:1474–1480
Mujoomdar A, Austin JH, Malhotra R, Powell CA, Pearson GD, Shiau MC, Raftopoulos H (2007) Clinical predictors of metastatic disease to the brain from non-small cell lung carcinoma: primary tumor size, cell type, and lymph node metastases. Radiology 242(3):882–888
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE (2004) Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer surveillance system. J Clin Oncol 22:2865–2872
Knisely JP, Berkey B, Chakravarti A, Yung AW, Curran WJ Jr, Robins HI, Movsas B, Brachman DG, Henderson RH, Mehta MP (2008) A phase III study of conventional radiation therapy plus thalidomide versus conventional radiation therapy for multiple brain metastases (RTOG 0118). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71:79–86
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG, Byhardt R (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:745–751
Khuntia D, Brown P, Li J et al (2006) Whole-brain radiotherapy in the management of brain metastasis. J Clin Oncol 24:1295–1304
Shepherd FA, Pereira JR, Ciuleanu T et al (2005) Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 353(2):123–132
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S et al (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361(10):947–957
Togashi Y, Masago K, Masuda S et al (2012) Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of gefitinib and erlotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 70:399–405
Wu YL, Zhou C, Cheng Y et al (2011) Erlotinib as second-line treatment in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and asymptomatic brain metastases: a phase II study (CTONG-0803). Lancet Oncol. 12:735–742
Ceresoli GL, Cappuzzo F, Gregorc V et al (2004) Gefitinib in patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer: a prospective trial. Ann Oncol 15:1042–1047
Welsh JW, Komaki R, Amini A et al (2013) Phase II trial of erlotinib plus concurrent whole-brain radiation therapy for patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 31:895–902
Kim JE, Lee DH, Choi Y et al (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors as a first-line therapy for never-smokers with adenocarcinoma of the lung having asymptomatic synchronous brain metastases. Lung Cancer 65:351–354
Iuchi T, Shingyoji M, Sakaida T et al (2013) Phase II trial of gefitinib alone without radiation therapy for Japanese patients with brain metastases from EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 82:282–287
Chinnaiyan P, Huang S, Vallabhaneni G et al (2005) Mechanisms of enhanced radiation response following epidermal growth factor receptor signaling inhibition by erlotinib (Tarceva). Cancer Res 65:3328–3335
Tan F, Shen X, Wang D et al (2012) Icotinib (BPI-2009H), a novel EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, displays potent efficacy in preclinical studies. Lung Cancer 76:177–182
Shi Y, Zhang L, Liu X et al (2013) Icotinib versus gefitinib in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (ICOGEN): a randomised, double-blind phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 14:953–961
Namba Y, Kijima T, Yokota S et al (2004) Gefitinib in patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer: review of 15 clinical cases. Clin Lung Cancer. 6:123–128
Garassino MC, Martelli O, Broggini M et al (2013) Erlotinib versus docetaxel as second-line treatment of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and wild-type EGFR tumours (TAILOR): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 14:981–988
Kawaguchi T, Ando M, Asami K et al (2014) Randomized phase III trial of erlotinib versus docetaxel as second- or third-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Docetaxel and Erlotinib Lung Cancer Trial (DELTA). J Clin Oncol 32:1902–1908
Zhou Q, Cheng Y, Yang JJ et al (2014) Pemetrexed versus gefitinib as a second-line treatment in advanced nonsquamous nonsmall-cell lung cancer patients harboring wild-type EGFR (CTONG0806): a multicenter randomized trial. Ann Oncol 25:2385–2391
Lee JK, Hahn S, Kim DW et al (2014) Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors vs. conventional chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer harboring wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor: a meta-analysis. JAMA 311:1430–1437
Soon YY, Leong CN, Koh WY et al (2015) EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors versus cranial radiation therapy for EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol 114(2):167–172
Icotinib treat the patient with brain metastases epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant non small cell lung cancer comparing with whole brain radiotherapy. http://www.ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01724801)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Huang, Z., Fang, L. et al. A phase II study of icotinib and whole-brain radiotherapy in Chinese patients with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 76, 517–523 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2760-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2760-5