Abstract
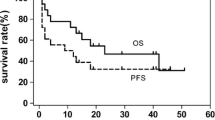
The prognosis of patients with stage III/IV NK/T-cell lymphoma (NTCL) is extremely poor. Although l-asparaginase (l-asp) is effective for NTCL, its significance has not been clearly demonstrated. In addition, there are few studies comparing treatment outcomes in stage III/IV NTCL. This study evaluated the efficacy of l-asp-based chemotherapy and prognostic factors in stage III/IV NTCL. Seventy patients with newly diagnosed stage III/IV NTCL were enrolled between January 2000 and February 2013. Patients received ifosfamide, etoposide, methotrexate, and prednisolone (IMEP) plus l-asp (N = 22) or combination chemotherapy without l-asp (N = 48) as a first-line treatment. Clinical prognostic factors, treatment outcomes, and prognostic scores were compared between the groups. After a median follow-up period of 12.8 months (range, 1.1–186.6 months), median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were 11.3 and 5.6 months, respectively. Treatment outcomes were superior in patients treated with IMEP plus l-asp compared to those treated with chemotherapy without l-asp (overall response rate, 90.0 vs. 34.8 %, P < 0.001; complete remission rate, 65.0 vs. 21.7 %, P = 0.001). The OS and PFS were significantly higher for the IMEP plus l-asp group compared with the chemotherapy without l-asp group. In a multivariate analysis, the use of chemotherapy without l-asp was an independent predictor of reduced OS (hazards ratio (HR) = 2.18, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.08–4.40; P = 0.030) and PFS (HR = 2.29, 95 % CI 1.22–4.29; P = 0.010). IMEP plus l-asp is active against stage III/IV NTCL, and it is an independent predictor of improved survival.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan JK, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ferry JA, Peh S-C (2008) Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL et al (eds) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. IARC, Lyon, pp 285–288
Kwong YL, Chan AC, Liang R, Chiang AK, Chim CS, Chan TK, Todd D, Ho FC (1997) CD56+ NK lymphomas: clinicopathological features and prognosis. Br J Haematol 97(4):821–829
Yamaguchi M, Kita K, Miwa H, Nishii K, Oka K, Ohno T, Shirakawa S, Fukumoto M (1995) Frequent expression of P-glycoprotein/MDR1 by nasal T-cell lymphoma cells. Cancer 76(11):2351–2356
Lee KW, Yun T, Kim DW, Im SA, Kim TY, Yoon SS, Heo DS, Bang YJ, Park S, Kim BK, Kim NK (2006) First-line ifosfamide, methotrexate, etoposide and prednisolone chemotherapy +/− radiotherapy is active in stage I/II extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 47(7):1274–1282. doi:10.1080/10428190600562823
Ando M, Sugimoto K, Kitoh T, Sasaki M, Mukai K, Ando J, Egashira M, Schuster SM, Oshimi K (2005) Selective apoptosis of natural killer-cell tumours by l-asparaginase. Br J Haematol 130(6):860–868. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05694.x
Kwong YL, Kim WS, Lim ST, Kim SJ, Tang T, Tse E, Leung AY, Chim CS (2012) SMILE for natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: analysis of safety and efficacy from the Asia Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 120(15):2973–2980. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-05-431460
Yamaguchi M, Kwong YL, Kim WS, Maeda Y, Hashimoto C, Suh C, Izutsu K, Ishida F, Isobe Y, Sueoka E, Suzumiya J, Kodama T, Kimura H, Hyo R, Nakamura S, Oshimi K, Suzuki R (2011) Phase II study of SMILE chemotherapy for newly diagnosed stage IV, relapsed, or refractory extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: the NK-Cell Tumor Study Group study. J Clin Oncol 29(33):4410–4416. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.35.6287
Jaccard A, Gachard N, Marin B, Rogez S, Audrain M, Suarez F, Tilly H, Morschhauser F, Thieblemont C, Ysebaert L, Devidas A, Petit B, de Leval L, Gaulard P, Feuillard J, Bordessoule D, Hermine O (2011) Efficacy of l-asparaginase with methotrexate and dexamethasone (AspaMetDex regimen) in patients with refractory or relapsing extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, a phase 2 study. Blood 117(6):1834–1839. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-09-307454
Chan JK, Jaffe ES, Ralfkiaer E (2001) Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (eds) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. IARC, Lyon, pp 204–207
Kim TM, Lee SY, Jeon YK, Ryoo BY, Cho GJ, Hong YS, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Kim CS, Kim S, Kim JS, Sohn SK, Song HH, Lee JL, Kang YK, Yim CY, Lee WS, Yuh YJ, Kim CW, Heo DS (2008) Clinical heterogeneity of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: a national survey of the Korean Cancer Study Group. Ann Oncol 19(8):1477–1484. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn147
Shipp MA, Harrington DP, Anderson JR, Armitage JO, Bonadonna G, Brittinger G, Cabanillas F, Canellos GP, Coiffier B, Connors JM, Cowan RA, Crowther D, Dahlberg S, Engelhard M, Fisher RI, Gisselbrecht C, Horning SJ, Lepage E, Lister TA, Meerwaldt JH, Monterrat E, Nissen NI, Oken MM, Peterson BA, Tondini C, Velasquez WA, Yeap BY (1993) A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. N Engl J Med 329(14):987–994
Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, Gascoyne RD, Specht L, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Fisher RI, Hagenbeek A, Zucca E, Rosen ST, Stroobants S, Lister TA, Hoppe RT, Dreyling M, Tobinai K, Vose JM, Connors JM, Federico M, Diehl V, International Harmonization Project on L (2007) Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25(5):579–586. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.09.2403
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observation. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life-table. J R Stat Soc Ser B 34:187–120
Nagafuji K, Fujisaki T, Arima F, Ohshima K (2001) l-asparaginase induced durable remission of relapsed nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma after autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol 74(4):447–450
Lin N, Song Y, Zheng W, Tu M, Xie Y, Wang X, Ping L, Ying Z, Zhang C, Deng L, Liu W, Zhu J (2013) A prospective phase II study of l-asparaginase- CHOP plus radiation in newly diagnosed extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. J Hematol Oncol 6(1):44. doi:10.1186/1756-8722-6-44
Yong W, Zheng W, Zhu J, Zhang Y, Wang X, Xie Y, Lin N, Xu B, Lu A, Li J (2009) l-asparaginase in the treatment of refractory and relapsed extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Hematol 88(7):647–652. doi:10.1007/s00277-008-0669-3
Jaccard A, Petit B, Girault S, Suarez F, Gressin R, Zini JM, Coiteux V, Larroche C, Devidas A, Thieblemont C, Gaulard P, Marin B, Gachard N, Bordessoule D, Hermine O (2009) l-asparaginase-based treatment of 15 western patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma and leukemia and a review of the literature. Ann Oncol 20(1):110–116. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn542
Kim BS, Kim TY, Kim CW, Kim JY, Heo DS, Bang YJ, Kim NK (2003) Therapeutic outcome of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma initially treated with chemotherapy—result of chemotherapy in NK/T-cell lymphoma. Acta Oncol 42(7):779–783
Suzuki R, Suzumiya J, Yamaguchi M, Nakamura S, Kameoka J, Kojima H, Abe M, Kinoshita T, Yoshino T, Iwatsuki K, Kagami Y, Tsuzuki T, Kurokawa M, Ito K, Kawa K, Oshimi K (2010) Prognostic factors for mature natural killer (NK) cell neoplasms: aggressive NK cell leukemia and extranodal NK cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Oncol 21(5):1032–1040. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp418
Kim BS, Kim DW, Im SA, Kim CW, Kim TY, Yoon SS, Heo DS, Bang YJ, Park S, Kim BK, Kim NK (2009) Effective second-line chemotherapy for extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma consisting of etoposide, ifosfamide, methotrexate, and prednisolone. Ann Oncol 20(1):121–128. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn551
Kim TM, Kim D-W, Kang Y-K, Song H-S, Kim HJ, Kim BS, Heo DS (2013) A phase II trial of ifosfamide, methotrexate, etoposide, and prednisolone (IMEP) for previously untreated stage I, II extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (NTCL): a multicenter study of the Korean Cancer Study Group. ASCO Meet Abstr 31:8521
Yang L, Liu H, Xu XH, Wang XF, Huang HM, Shi WY, Jiang SH (2013) Retrospective study of modified SMILE chemotherapy for advanced-stage, relapsed, or refractory extranodal natural killer (NK)/T cell lymphoma, nasal type. Med Oncol 30(4):720. doi:10.1007/s12032-013-0720-7
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Shipp MA, Fisher RI, Connors JM, Lister TA, Vose J, Grillo-Lopez A, Hagenbeek A, Cabanillas F, Klippensten D, Hiddemann W, Castellino R, Harris NL, Armitage JO, Carter W, Hoppe R, Canellos GP (1999) Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol 17(4):1244–1253
Schrey D, Borghorst S, Lanvers-Kaminsky C, Hempel G, Gerss J, Moricke A, Schrappe M, Boos J (2010) Therapeutic drug monitoring of asparaginase in the ALL-BFM 2000 protocol between 2000 and 2007. Pediatr Blood Cancer 54(7):952–958. doi:10.1002/pbc.22417
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Innovative Research Institute for Cell Therapy, Republic of Korea (A062260). We thank Juyoun Kim for the assistance with clinical data collection.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M., Kim, T.M., Kim, K.H. et al. Ifosfamide, methotrexate, etoposide, and prednisolone (IMEP) plus l-asparaginase as a first-line therapy improves outcomes in stage III/IV NK/T cell-lymphoma, nasal type (NTCL). Ann Hematol 94, 437–444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2228-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2228-4