Abstract
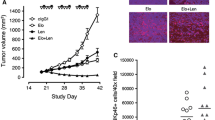
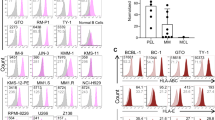
Elotuzumab is a monoclonal antibody in development for multiple myeloma (MM) that targets CS1, a cell surface glycoprotein expressed on MM cells. In preclinical models, elotuzumab exerts anti-MM efficacy via natural killer (NK)-cell-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). CS1 is also expressed at lower levels on NK cells where it acts as an activating receptor. We hypothesized that elotuzumab may have additional mechanisms of action via ligation of CS1 on NK cells that complement ADCC activity. Herein, we show that elotuzumab appears to induce activation of NK cells by binding to NK cell CS1 which promotes cytotoxicity against CS1(+) MM cells but not against autologous CS1(+) NK cells. Elotuzumab may also promote CS1–CS1 interactions between NK cells and CS1(+) target cells to enhance cytotoxicity in a manner independent of ADCC. NK cell activation appears dependent on differential expression of the signaling intermediary EAT-2 which is present in NK cells but absent in primary, human MM cells. Taken together, these data suggest elotuzumab may enhance NK cell function directly and confer anti-MM efficacy by means beyond ADCC alone.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiner LM, Dhodapkar MV, Ferrone S (2009) Monoclonal antibodies for cancer immunotherapy. Lancet 373:1033–1040
Richardson PG, Lonial S, Jakubowiak AJ, Harousseau JL, Anderson KC (2011) Monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 154:745–754
Tai Y-T, Dillon M, Song W et al (2008) Anti-CS1 humanized monoclonal antibody HuLuc63 inhibits myeloma cell adhesion and induces antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in the bone marrow milieu. Blood 112:1329–1337
Hsi ED, Steinle R, Balasa B et al (2008) CS1, a potential new therapeutic antibody target for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 14:2775–2784
Stark S, Watzl C (2006) 2B4 (CD244), NTB-A, and CRACC (CS1) stimulate cytotoxicity but no proliferation in human NK cells. Int Immunol 18:241–247
Cruz-Munoz M-E, Dong Z, Shi X, Zhang S, Veillette A (2009) Influence of CRACC, a SLAM family receptor coupled to the adaptor EAT-2, on natural killer cell function. Nat Immunol 10:297–305
Tassi I, Colonna M (2005) The cytotoxicity receptor CRACC (CS-1) recruits EAT-2 and activates the PI3 K and phospholipase Cgamma signaling pathways in human NK cells. J Immunol 175:7996–8002
Benson DM Jr, Bakan CE, Mishra A et al (2010) The PD-1/PD-L1 signaling axis modulates the natural killer cell versus multiple myeloma effect: a therapeutic target for CT-011, a novel monoclonal anti-PD-1 antibody. Blood 116:2286–2294
Zonder JA, Mohrbacher AF, Singhal S et al (2012) A Phase I multicenter, open-label, dose escalation study of elotuzumab in patients with advanced multiple myeloma. Blood 120:552–559
Jakubowiak AJ, Benson DM, Bensinger W et al (2012) Phase I trial of anti-CS1 antibody elotuzumab in combination with bortezomib in the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 30:1960–1965
Lonial S, Vig R, Harousseau JL et al (2012) Elotuzumab in combination with lenalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 30:1953–1959
Shafer-Weaver KA, Sayers T, Kuhns DB et al (2004) Evaluating the cytotoxicity of innate immune effector cells using the GrB ELISPOT assay. J Trans Med 2:31–36
Benson DM Jr, Bakan CE, Zhang S et al (2011) IPH2101, a novel anti-inhibitory KIR antibody, and lenalidomide combine to enhance the natural killer cell versus multiple myeloma effect. Blood 118:6387–6391
Trotta R, Puorro KA, Paroli M et al (1998) Dependence of both spontaneous and antibody-dependent, granule exocytosis-mediated NK cell cytotoxicity on extracellular signal-regulated kinases. J Immunol 161:6648–6656
Benson DM Jr, Yu J, Becknell B et al (2009) Stem cell factor and interleukin-2/15 combine to enhance MAPK-mediated proliferation of human natural killer cells. Blood 113:2706–2714
Fehniger TA, Shah MH, Turner MJ et al (1999) Differential cytokine and chemokine gene expression by human NK cells following activation with IL-18 or IL-15 in combination with IL-12: implications for the innate immune response. J Immunol 162:4511–4520
Freud AG, Yokohama A, Becknell B et al (2006) Evidence for discrete stages of human natural killer cell differentiation in vivo. J Exp Med 203:1033–1043
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA (2001) The biology of human natural killer cell subsets. Trends Immunol 22:633–640
Cao E (2006) NTB-A receptor crystal structure: insights into homophilic interactions in the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule receptor family. Immunity 25:559–570
Kondadasula SV, Varker K, Lesinski GB et al (2008) Activation of extracellular signaling regulated kinase in natural killer cells and monocytes following IL-2 stimulation in vitro and in patients undergoing IL-2 immunotherapy: analysis via dual parameter flow cytometric assay. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57:1137–1149
Davies FE, Raje N, Hideshima T et al (2001) Thalidomide and immunomodulatory derivatives augment natural killer cell cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma. Blood 98:210–216
Shi J, Tricot G, Garg TK et al (2008) Bortezomib down-regulates the cell surface expression of HLA-class I and enhances natural killer cell mediated lysis of myeloma. Blood 111:1309–1317
Neyer L, Ding H, Chen D et al (2010) Effect of elotuzumab on circulating lymphocytes, chemokines and cytokines in multiple myeloma patients. Blood 116:4070a
Balasa B, Huseni M, Cherukuri J et al (2008) Elotuzumab (HuLuc63) activates CD56dim natural killer cells and monocytes resulting in the release of IP-10 and MCP-1. Blood 112:108a
Rice AG, Dillon MBC, Van Abbema AM, Afar DEH (2007) HuLuc63 in combination regimens with conventional and targeted therapies has additive and synergistic anti-tumor activity in pre-clinical models of myeloma. Blood 110:2517a
Balasa B, Yun R, Belmar N, Starling G, Rice A (2012) Natural killer (NK) cell activation, cytokine production and cytotoxicity in human PBMC/myeloma cell co-culture exposed to elotuzumab (Elo) alone or in combination with lenalidomide (len). J Clin Oncol 30:8087a
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by funding from Pelotonia Undergraduate Fellowship Program (Shauna M Collins, Don M Benson, Jr) and Multiple Myeloma Opportunities for Research and Education (Don M Benson, Jr, Craig C Hofmeister, Yvonne A Efebera).
Conflict of interest
Don M Benson has served in an advisory capacity to and received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb; Gary C Starling is a former employee of Abbott Laboratories; Hakju Kwon and Audie Rice are employees of Abbvie Biotherapeutics Inc. No other authors have conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collins, S.M., Bakan, C.E., Swartzel, G.D. et al. Elotuzumab directly enhances NK cell cytotoxicity against myeloma via CS1 ligation: evidence for augmented NK cell function complementing ADCC. Cancer Immunol Immunother 62, 1841–1849 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-013-1493-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-013-1493-8