Abstract
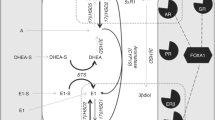
The sulfatase pathway has been thought to be a primary means of local production of estrone in human breast cancer tissue. We measured steroid sulfatase (STS) mRNA levels in 97 breast cancers and evaluated its association with disease-free survival. High levels of STS mRNA proved to be a significant predictor of reduced relapse-free survival, both as a continuous variable (log STS mRNA; P=0.028) and as a dichotomous variable with an optimized cutoff point (P=0.002). In multivariate analysis a high level of STS mRNA was an independent factor for predicting relapse-free survival. These results suggest a putative role of STS in breast cancer growth and metastasis, and administration of sulfatase inhibitors to breast cancer patients with high levels of STS mRNA might be an additional treatment option.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- STS:
-
Steroid sulfatase
References
Edery M, Goussard J, Dehennin L,et al: Endogenous oestradiol-17β concentration in breast tumours determined by mass fragmentography and by radioimmunoassay; Relationship to receptor content.Eur J Cancer 17:115–120, 1981.
Millington DS: Determination of hormonal steroid concentrations in biological extracts by high resolution mass fragmentography.J Steroid Biochem 6:239–245, 1975.
van Landeghem AA, Poortman J, Nabuurs M,et al: Endogenous concentration and subcellular distribution of estrogens in normal and malignant human breast tissue.Cancer Res 45:2900–2906, 1985.
Santner SJ, Feil PD, Santen RJ: In situ estrogen production via the estrone sulfatase pathway in breast tumors; Relative importance versus the aromatase pathway.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 59:29–33, 1984.
Pasqualini JR, Gelly C, Nguyen BL,et al: Importance of estrogen sulfates in breast cancer.J Steroid Biochem 34:155–163, 1989.
Utsumi T: Local production of estrogen via aromatase and estrone sulfatase in breast cancer tissue.J Jap Surg Soc 90:920–927, 1989 (in Japanese with English abstract).
Vermeulen A, Deslypere JP, Paridaens R,et al: Aro matase, 17 β -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and intratissular sex hormone concentrations in cancerous and normal glandular breast tissue in postmenopausal women.Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 22:515–525, 1986.
Utsumi T, Harada N, Maruta M,et al: Presence of alternatively spliced transcripts of aromatase gene in human breast cancer.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:2344–2349, 1996.
Ruder HJ, Loriaux L, Lipsett MB: Estrone sulfate; Production rate and metabolism in man.J Clin Invest 51:1020–1033, 1972.
Gniot-Szulzycka J, Januszewska B: Purification of steroid sulphohydrolase from human placenta microsomes.Acta Biochim Pol 33:203–215, 1986.
Prost O, Turrel MO, Dahan N,et al: Estrone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfatase activities and plasma estrone sulfate levels in human breast carcinoma.Cancer Res 44:661–664, 1984.
Dibbelt L, Kuss E: Human placental steryl-sulfatase; Enzyme purification, production of antisera, and immunoblotting reactions with normal and sulfatasedeficient placentas.Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 367:1223–1229, 1986.
Ballabio A, Parenti G, Carrozzo R,et al: Isolation and characterization of a steroid sulfatase cDNA clone; Genomic deletions in patients with X-chromosomelinked ichthyosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4519–4523, 1987.
Kawano J, Kotani T, Ohtaki S,et al: Characterization of rat and human steroid sulfatases.Biochim Biophys Acta 997:199–205, 1989.
Yen PH, Allen E, Marsh B,et al: Cloning and expression of steroid sulfatase cDNA and the frequent occurrence of deletions in STS deficiency; Implications for X-Y interchange.Cell 49:443–454, 1987.
Utsumi T, Yoshimura N, Takeuchi S,et al: Steroid sulfatase expression is an independent predictor of recurrence in human breast cancer.Cancer Res 59:377–381, 1999.
Selcer KW, Hegde PV, Li PK: Inhibition of estrone sulfatase and proliferation of human breast cancer cells by nonsteroidal (p-O-sulfamoyl)-N-alkanoyl tyra-mines.Cancer Res 57:702–707, 1997.
Purohit A, Williams GJ, Howarth NM,et al: Inactivation of steroid sulfatase by an active site-directed inhibitor, estrone-3-O-sulfamate.Biochemistry 34:11508–1514, 1995.
Purohit A, Woo LW, Singh A,et al: In vivo activity of 4-methylcoumarin-7-0-sulfamate, a nonsteroidal, nonestrogenic steroid sulfatase inhibitor.Cancer Res 56:4950–4955, 1996.
Kolli A, Chu GH, Rhodes ME,et al: Development of (p-O-sulfamoyl)-N-alkanoyl-phenylalkyl amines as non-streroidal estrone sulfatase inhibitors.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 68:31–40, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Utsumi, T., Yoshimura, N., Maruta, M. et al. Significance of steroid sulfatase expression in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer 6, 298–300 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02966443
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02966443